Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using the necessary circuit diagrams, show how the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction are obtained in
Reverse biasing
How are these characteristics made use of in rectification?
उत्तर
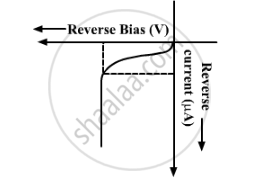
p-n junction diode under reverse bias

Positive terminal of battery is connected to n-side and negative terminal to p-side.
Reverse bias supports the potential barrier. Therefore, the barrier height increases and the width of depletion region also increases.
Due to the majority carriers, there is no conduction across the junction. A few minority carriers cross the junction after being accelerated by high reverse bias voltage.
This constitutes a current that flows in opposite direction, which is called reverse current.
The V-I characteristics of p-n junction diode in reverse bias is shown below:
p-n junction diode is used as a half-wave rectifier. Its working is based on the fact that the resistance of p-n junction becomes low when forward biased and becomes high when reverse biased. These characteristics of diode is used in rectification.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Meeta's father was driving her to school. At the traffic signal, she noticed that each traffic light was made of many tiny lights instead of a single bulb. When Meeta asked this question to her father, he explained the reason for this.
Answer the following questions based on above information:
(i) What were the values displayed by Meeta and her father?
(ii) What answer did Meeta's father give?
(iii) What are the tiny lights in traffic signals called and how do these operate?
Write briefly the important processes that occur during the formation of p−n junction. With the help of necessary diagrams, explain the term 'barrier potential'.
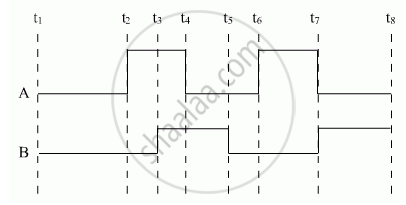
Show the output waveforms (Y) for the following inputs A and B of (i) OR gate (ii) NAND gate ?
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in reverse bias. Plot the V-I characteristics in this case.
What is a solar cell?
Which one of the following is not the advantage of LED?
Consider the following statements (A) and (B) and identify the correct answer.
- A Zener diode is connected in reverse bias when used as a voltage regulator.
- The potential barrier of the p-n junction lies between 0.1 V to 0.3 V.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
|
LED is a heavily doped P-N junction which under forward bias emits spontaneous radiation. When it is forward-biased, due to recombination of holes and electrons at the junction, energy is released in the form of photons. In the case of Si and Ge diode, the energy released in recombination lies in the infrared region. LEDs that can emit red, yellow, orange, green and blue light are commercially available. The semiconductor used for fabrication of visible LEDs must at least have a band gap of 1.8 eV. The compound semiconductor Gallium Arsenide – Phosphide is used for making LEDs of different colours.
|
- Why are LEDs made of compound semiconductor and not of elemental semiconductors?
- What should be the order of bandgap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range?
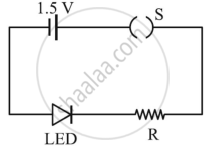
- A student connects the blue coloured LED as shown in the figure. The LED did not glow when switch S is closed. Explain why?
OR
iii. Draw V-I characteristic of a p-n junction diode in
(i) forward bias and (ii) reverse bias
Draw solar cells of I-V characteristics.
What energy conversion takes place in a solar cell?

