Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent?
HI
उत्तर
When D-glucose is heated with HI for a long time, n-hexane is formed.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CHO}\phantom{...............................................}\\
|\phantom{..................................................}\\
\ce{(CHOH)4 ->[HI][\Delta] \underset{{n}-hexane}{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - CH3}}\\
|\phantom{..................................................}\\
\ce{\underset{{D-glucose}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{..........................................}
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the reaction that indicates the presence of -CHO group in glucose
Maltose is a
(a) Polysaccharide
(b) Disaccharide
(c) Trisaccharide
(d) Monosaccharide
What do you observe when glucose solution is heated with Tollen’s reagent?
Write the reactions involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent:
(CH3CO)2O
The following compound can be called as:
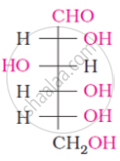
The spatial arrangement of the given molecule is denoted by:

Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding glucose?
Glucose does not react with ____________.
A solution of D-glucose in water rotates the plane polarised light ____________.
The number of chiral carbon atoms present in cyclic structure α-D(+) glucose:
The letter D and L in carbohydrates represent ____________.
The number of chiral carbons in ß-D(+) glucose is ____________.
In the following reaction, identify A and B:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C6H12O6 ->[Acetic anhydride] A}\\
\downarrow \text{Conc. nitric acid}\phantom{...}\\
\ce{B}\phantom{.................}\end{array}\]
Why does compound (A) given below not form an oxime?
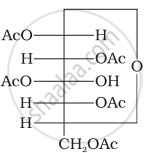
(A)
How will you distinguish 1° and 2° hydroxyl groups present in glucose? Explain with reactions.
Consider the following reactions:
(i) \[\ce{Glucose + R-OH ->[Conc. HNO3] [A] ->[X eq of][(CH3CO)2O] Acetyl derivative}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Glucose ->[Ni/H2] [A] ->[Y eq of][(CH3CO)2O] Acetyl derivative}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Glucose ->[Z eq of][(CH3CO)2O] Acetyl derivative}\]
'X, 'Y' and 'Z' in these reactions are respectively:
The number of asymmetric carbon atoms in the glucose molecule in open and cyclic form is ______.
Match List - I with List - II.
| List I | List II | ||
| (A) | Glucose + HI | (I) | Gluconic acid |
| (B) | Glucose + Br2 water | (II) | Glucose pentacetate |
| (C) | Glucose + acetic anhydride | (III) | Saccharic acid |
| (D) | Glucose + HNO3 | (IV) | Hexane |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
