Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which inert gas does the Cl atom in HCl resemble in electron arrangement?
उत्तर
The Cl atom in HCl resembles argon gas in its electron arrangement by sharing one electron with the hydrogen atom to get eight electrons in its outermost shell. Its electronic configuration becomes 2, 8, 8.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What type of bonds are present in Cl2 molecule? Draw their electron-dot structures.
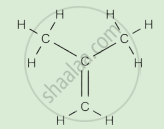
Give one example of a molecule containing a double covalent bond
Draw the electron-dot structure of NH3 and state the type of bonding.
What is graphite?
The pencil leads are made of mainly:
(a) lithium
(b) charcoal
(c) lead
(d) graphite
Give two example in following case:
Solid covalent compounds
The following structural formula belongs to which carbon compound?
Explain the structure of Hydronium ion.
Acids dissolve in water to produce positively charged ions. Draw the structure of these positive ions.
The electronic configuration of N2 is 2, 5. How many electrons in the outer shell of a N atom are not involved in the formation of a nitrogen molecule?
Explain the bonding in methane molecule using electron dot structure.
Acids dissolve in water and produce positively charged ions. Draw the structure of these positive ions.
What are Allotropes? Name any two allotropic forms of carbon. Give one use of it.
Fill in the blank and rewrite the completed statement:
Covalent compounds are generally soluble in _________ solvents.
Complete the following activity.
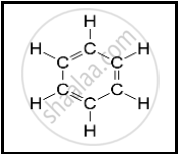
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
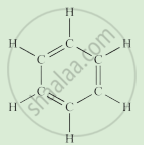 |
Complete the following activity.
Write the names of the hydrocarbons for the following structural formula.
(isobutylene, cyclohexane, propene, cyclohexene, cyclopentane, benzene, propyne, isobutane, propane)
 |
Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
- \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{.....}|\\
\ce{H}\ce{H-C-H}\ce{H}\\
|\\
\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{.....}\backslash\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{H}\phantom{......}\ce{C - H}\phantom{}\\
\phantom{.......}|\\
\phantom{.......}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\] - \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H - C - C - H}\\
|\phantom{....}|\\
\ce{H}\phantom{...}\ce{H}\\
\end{array}\]
______ is an example of a covalent compound having a high melting point.
Molecular reactions are ______ in the covalent compound.
