Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Which of the following can be the sides of a right triangle?
2 cm, 2 cm, 5 cm
In the case of right-angled triangles, identify the right angles.
उत्तर
2 cm, 2 cm, 5 cm
(2)2 = 4
(2)2 = 4
(5)2 = 25
Here, (2)2 + (2)2 ≠ (5)2
The square of the length of one side is not equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the remaining two sides. Hence, these sides are not of a right-angled triangle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a right triangle ABC right-angled at C, P and Q are the points on the sides CA and CB respectively, which divide these sides in the ratio 2 : 1. Prove that
`(i) 9 AQ^2 = 9 AC^2 + 4 BC^2`
`(ii) 9 BP^2 = 9 BC^2 + 4 AC^2`
`(iii) 9 (AQ^2 + BP^2 ) = 13 AB^2`
In an isosceles triangle, length of the congruent sides is 13 cm and its base is 10 cm. Find the distance between the vertex opposite the base and the centroid.
O is any point inside a rectangle ABCD.
Prove that: OB2 + OD2 = OC2 + OA2.
In the right-angled ∆PQR, ∠ P = 90°. If l(PQ) = 24 cm and l(PR) = 10 cm, find the length of seg QR.
Find the length of the hypotenuse of a triangle whose other two sides are 24cm and 7cm.
In an equilateral triangle ABC, the side BC is trisected at D. Prove that 9 AD2 = 7 AB2.
In the given figure, PQ = `"RS"/(3)` = 8cm, 3ST = 4QT = 48cm.
SHow that ∠RTP = 90°.
Find the unknown side in the following triangles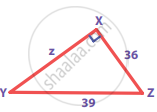
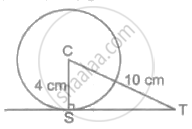
In the adjoining figure, a tangent is drawn to a circle of radius 4 cm and centre C, at the point S. Find the length of the tangent ST, if CT = 10 cm.
The perimeter of the rectangle whose length is 60 cm and a diagonal is 61 cm is ______.
