Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
O is any point inside a rectangle ABCD.
Prove that: OB2 + OD2 = OC2 + OA2.
उत्तर
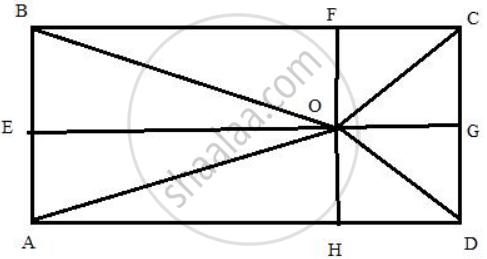
Draw rectangle ABCD with arbitrary point O within it, and then draw lines OA, OB, OC, OD. Then draw lines from point O perpendicular to the sides: OE, OF, OG, OH.
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the remaining two sides.
Using Pythagorean theorem we have from the above diagram:
OA2 = AH2 + OH2 = AH2 + AE2
OC2 = CG2 + OG2 = EB2 + HD2
OB2 = EO2 + BE2 = AH2 + BE2
OD2 = HD2 + OH2 = HD2 + AE2
Adding these equalities we get:
OA2 + OC2 = AH2 + HD2 + AE2 + EB2
OB2 + OD2 = AH2 + HD2 + AE2 + EB2
From which we prove that for any point within the rectangle there is the relation
OA2 + OC2 = OB2 + OD2
Hence Proved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In Figure, ABD is a triangle right angled at A and AC ⊥ BD. Show that AB2 = BC × BD
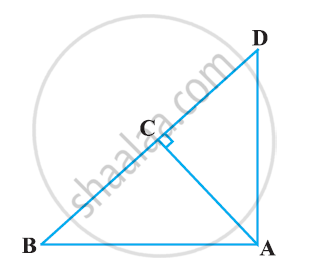
In an equilateral triangle ABC, D is a point on side BC such that BD = `1/3BC` . Prove that 9 AD2 = 7 AB2
In the given figure, ∆ABC is an equilateral triangle of side 3 units. Find the coordinates of the other two vertices ?
Identify, with reason, if the following is a Pythagorean triplet.
(24, 70, 74)
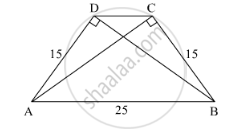
In a trapezium ABCD, seg AB || seg DC seg BD ⊥ seg AD, seg AC ⊥ seg BC, If AD = 15, BC = 15 and AB = 25. Find A(▢ABCD)
AD is drawn perpendicular to base BC of an equilateral triangle ABC. Given BC = 10 cm, find the length of AD, correct to 1 place of decimal.
In equilateral Δ ABC, AD ⊥ BC and BC = x cm. Find, in terms of x, the length of AD.
Diagonals of rhombus ABCD intersect each other at point O.
Prove that: OA2 + OC2 = 2AD2 - `"BD"^2/2`
Prove that in a right angle triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
In the given figure, angle BAC = 90°, AC = 400 m, and AB = 300 m. Find the length of BC.

Show that the triangle ABC is a right-angled triangle; if: AB = 9 cm, BC = 40 cm and AC = 41 cm
In the figure below, find the value of 'x'.
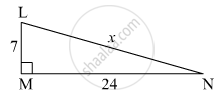
In the figure below, find the value of 'x'.
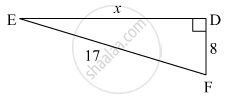
Find the Pythagorean triplet from among the following set of numbers.
9, 40, 41
Find the length of the perpendicular of a triangle whose base is 5cm and the hypotenuse is 13cm. Also, find its area.
In a triangle ABC, AC > AB, D is the midpoint BC, and AE ⊥ BC. Prove that: AB2 + AC2 = 2AD2 + `(1)/(2)"BC"^2`
In a triangle ABC, AC > AB, D is the midpoint BC, and AE ⊥ BC. Prove that: AC2 - AB2 = 2BC x ED
In a right angled triangle, if length of hypotenuse is 25 cm and height is 7 cm, then what is the length of its base?
In an isosceles triangle PQR, the length of equal sides PQ and PR is 13 cm and base QR is 10 cm. Find the length of perpendicular bisector drawn from vertex P to side QR.
If the areas of two circles are the same, they are congruent.
