Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
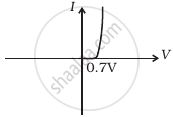
Why is a zener diode considered as a special purpose semiconductor diode?
उत्तर
Zener diode works only in reverse breakdown region that’s why it in considered as a special purpose semiconductor.
संबंधित प्रश्न
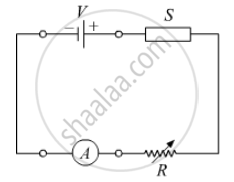
In the following diagram 'S' is a semiconductor. Would you increase or decrease the value of R to keep the reading of the ammeter A constant when S is heated? Give reason for your answer.
With reference to semiconductor devices, define a p-type semiconductor and a Zener diode.
Draw a labelled diagram of a full wave rectifier. Show how output voltage varies with time if the input voltage is a sinusoidal voltage.
With reference to semi-conductors answer the following :
(i) What is the change in the resistance of the semi-conductor with increase in temperature ?
(ii) Name the majority charge carriers in n-type semi-conductor.
(iii) What is meant by doping ?
The plate current in a diode is 20 mA when the plate voltage is 50 V or 60 V. What will be the current if the plate voltage is 70 V?
The power delivered in the plate circular of a diode is 1.0 W when the plate voltage is 36 V. Find the power delivered if the plate voltage is increased to 49 V. Assume Langmuir-Child equation to hold.
On increasing the reverse biases voltage to a large value in a P – N junction diode-current
Figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?

At Vi = 0.4 V, transistor is in active state.
At Vi = 1 V, it can be used as an amplifier.
At Vi = 0.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned off.
At Vi = 2.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned on.
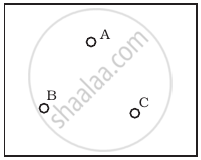
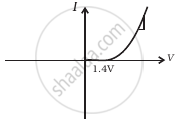
Consider a box with three terminals on top of it as shown in figure (a):
 (a) |
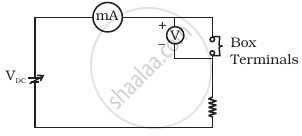
Three components namely, two germanium diodes and one resistor are connected across these three terminals in some arrangement. A student performs an experiment in which any two of these three terminals are connected in the circuit shown in figure (b).
 (b) |
The student obtains graphs of current-voltage characteristics for unknown combination of components between the two terminals connected in the circuit. The graphs are
(i) when A is positive and B is negative
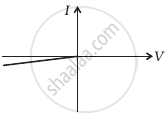 (c) |
(ii) when A is negative and B is positive
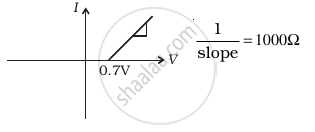 (d) |
(iii) When B is negative and C is positive
|
(e) |
(iv) When B is positive and C is negative
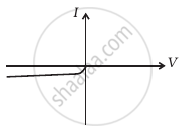 (f) |
(v) When A is positive and C is negative
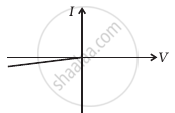 (g) |
(vi) When A is negative and C is positive
 (h) |
From these graphs of current-voltage characteristics shown in figure (c) to (h), determine the arrangement of components between A, B and C.
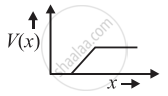
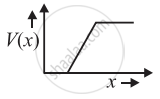
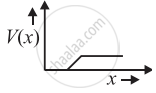
The graph of potential barrier versus width of depletion region for an unbiased diode is shown in graph A. In comparison to A, graphs B and C are obtained after biasing the diode in different ways. Identify the type of biasing in B and C and justify your answer
| ‘A’ | ‘B’ | ‘C’ |
 |
 |
 |