Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write advantages of science of heredity.
उत्तर
The advantages of the science of heredity are as follows:
- Diagnosis of diseases.
- Treatment and prevention of heredity disorders.
- Production of hybrid varieties of animals and plants.
- Industrial processes in which microbes are used.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How do Mendel’s experiments show that the traits may be dominant or recessive?
In one of his experiments with pea plants, Mendel observed that when a pure tall pea plant is crossed with a pure dwarf pea plant in the first generation, F1, only tall plants appear.
(a) What happens to the traits of the dwarf plants in this case?
(b) When the F1-generation plants were self-fertilised, he observed that in the plants of the second generation, F2, both tall plants and dwarf plants were present. Why it happened? Explain briefly.
How did Mendel interpret his results to show that traits may be dominant or recessive? Describe briefly.
A pea plant with blue colour flower denoted by BB is cross-bred with a pea plant with white flower denoted by ww.
(a) What is the expected colour of the flowers in their F1 progeny?
(b) What will be the percentage of plants bearing white flower in F2 generation, when the flowers of F1 plants were selfed?
(c) State the expected ratio of the genotype BB and Bw in the F2 progeny.
Define heredity.
List any two contrasting characters other than height that Mendel used in his experiments in pea plants.
List any two contrasting characters other than roundness of pea plants that Mendel used in his experiments with pea plants.
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits – blood group A or O – is dominant? Why or why not?
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as:
Outline a project which aims to find the dominant coat colour in dogs.
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding pea plants bearing violet flowers with pea plants bearing white flowers. What will be the result in F1 progeny?
What constitutes the link between one generation and the next?
Mendel said that the characteristics or traits of organisms are carried from one generation to the next by internal factors which occur in pairs. What is the modern name for these factors?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word .
In pea plants, the gene for dwarfness is ..............whereas that for tallness is ............ .
Name the scientist who gave the laws of inheritance.
Using height (tallness/dwarfness) of a plant as an example, show that genes control the characteristics or traits in an organism.
It it an example of monohybrid cross or dihybrid cross?
What is the genotype of tall plants which always produced tall offspring
Gregor Mendel's first law of genetics states "Of a pair of contrasted characters, only one can be represented in a gamete by its internal 'factor Give the modern name for this 'factor'.
Why did Mendel choose pea plants for conducting his experiments on inheritance?
A cross between two individuals results in a ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 for four possible phenotypes of progeny. This is an example of a ______
In order to ensure that he had pure-breeding plants for his experiments, Mendel :
(a) cross-fertilised each variety with each other
(b) let each variety self fertilise for several generations
(c) removed the female parts of the plants
(d) removed the male parts of the plants.
Select the statements that describe characteristics of genes :
(i) genes are specific sequences of bases in a DNA molecule.
(ii) a gene does not code for proteins.
(iii) in individuals of a given species, a specific gene is located on a particular chromosome.
(iv) each chromosome has only one gene..
In humans, if gene B gives brown eyes and gene b gives blue eyes. What will be the colour of eyes of the persons having the following combination of genes?
(a) Bb
(b) bb
(c) BB
Pure-bred pea plants A are crossed with pure-bred pea plants B. It is found that the plants which look like A do not appear in F1 generation but re-emerge in F2 generation. Which of the plants A and B are : (i) tall, and (ii) dwarf? Give reason for your answer.
A red-haired woman marries a brown-haired man, and all the children are brown haired. Explain this genetically.
A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group O and their daughter has blood group O. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits-blood group A or O - is dominant? Why or why not?
One of the following traits cannot be inherited. This one is :
(a) colour of eyes
(b) colour of skin
(c) size of body
(d) nature of hair
The farmers have been cultivating a food plant X for over two thousand years and have produced as many as five entirely different looking vegetables A, B, C, D and E from it.
(a) What could the plant X be?
(b) What are A, B, C, D and E?
(c) What is the process of evolution involved in this example known as?
List two differences in tabular form between dominant trait and recessive traits. What percentage/proportion of the plants in the F2 generation/progeny were round, in Mendel's cross between round and wrinkled pea plants?
If we pure-bred tall (dominant) pea plant with pure-bred dwarf (recessive) pea plant we will get pea plants of F1 generation. If we now self-cross the pea plant of F1 generation, then we obtain pea plants of F2 generation.
(a) What do the plants of F2 generation look like?
(b) State the ratio of tall plants to dwarf plants in F2 generation.
(c) State the type of plants not found in F1 generation but appeared in F2 generation, mentioning the reason for the same.
Explain Mendel’s law of independent inheritance. Give one example.
____________ refers to the transmission of genetic information from parental generation to next generation.
Two pink coloured flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red, 2 pink and 1 white flower progeny. The nature of the cross will be
A cross between a tall plant (TT) and short pea plant (tt) resulted in progeny that were all tall plants because
What are the components of the DNA molecule?
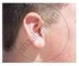
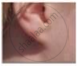
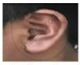
Figures (a) to (d) given below represent the type of ear lobes present in a family consisting of 2 children - Rahul, Nisha and their parents.
|
(a) Rahul's Father |
(b) Rahul |
(c) Rahul's Mother |
(d) Rahul's sister Nisha |
|
(e) |
(f) |
||
| Types of ear lobes | |||
Excited by his observation of different types of ear lobes present in his family, Rahul conducted a survey of the type of ear lobes found {Figure (e) and (f)} in his classmates. He found two types of ear lobes in his classmates as per the frequency given below:
| Sex | Free | Attached |
| Male | 36 | 14 |
| Female | 31 | 19 |
On the basis of the above data answer the following questions.
- Which of the two characteristics - ‘free ear lobe’ or ‘attached ear lobe’ appears to be dominant in this case? Why?
- Is the inheritance of the free ear lobe linked with the sex of the individual? Give a reason for your answer.
- What type of ear lobe is present in father, mother, Rahul and his sister Nisha? Write the genetic constitution of each of these family members which explains the inheritance of this character in this family.
(Gene for the Free ear lobe is represented by F and the gene for the attached ear lobe is represented by f for writing the genetic constitution).
OR
Suresh’s parents have attached ear lobes. What type of ear lobe can be seen in Suresh and his sister Siya? Explain by giving the genetic composition of all.