Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Chemical Bonding
3: Acids, Bases and Salts
4: Analytical Chemistry
5: Mole concept and Stoichiometry
6: Electrolysis
7: Metallurgy
8: Study of Compounds A - Hydrogen Chloride
9: Study of Compounds B - Ammonia
▶ 10: Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid
11: Study of Compounds D - Sulphuric Acid
12: Organic Chemistry
13: Practical Work
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-10-icse_6:a11ba386c5de4fb5831d789b303b585d.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 10: Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 10 of CISCE Selina for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE 10 Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid lntext Questions [Pages 168 - 169]
What is aqua fortis?
What is aqua regia?
What is fixation of Nitrogen?
During thunderstorm, rain water contains nitric acid. Explain with reactions.
Ammonia is used in the Ostwald process.
Give the sources of reactants used in this process.
Ammonia is used in the Ostwald process.
Name the catalyst used in the process.
Ammonia is used in the Ostwald process.
Name the oxidising agent used in this process.
Ammonia is used in the Ostwald process.
What is the ratio of ammonia and air taken in this process?
Ammonia is used in the Ostwald process.
Why is quartz used in this process?
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the laboratory preparation of nitric acid.
- In the preparation of nitric acid from \[\ce{KNO3}\], concentrated hydrochloric acid is not used in place of concentrated sulphuric acid. Explain why?
- Conc. nitric acid prepared in laboratory is yellow in colour. Why? How is this colour removed?
- Give reasons for the following:
In the laboratory preparation of nitric acid, the mixture of concentrated sulphuric acid and sodium nitrate should not be heated very strongly above 200°C.
Nitric acid cannot be concentrated beyond 68% by the distillation of a dilute solution of \[\ce{HNO3}\]. State the reason.
What is passive iron?
How is passivity removed?
Name the products formed when carbon and conc. nitric acid is heated.
Name the products formed when dilute \[\ce{HNO3}\] is added to copper.
Give two chemical equations for the following:
Reactions of nitric acid with non-metals
Give two chemical equations for the following:
Nitric acid showing as acidic character.
Give two chemical equations for the following:
Nitric acid acting as the oxidizing agent
Write a balanced equation and name the products formed when sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to nitric acid.
Write a balanced equation and name the products formed when cupric oxide reacts with nitric acid.
Write a balanced equation and name the products formed when concentrated nitric acid is heated.
How will you prepare the following from nitric acid?
Sodium nitrate
How will you prepare the following from nitric acid?
copper nitrate
How will you prepare the following from nitric acid?
Lead nitrate
How will you prepare the following from nitric acid?
Magnesium nitrate
How will you prepare the following from nitric acid?
Ferric nitrate
How will you prepare the following from nitric acid?
Aqua regia
Write equation for the following conversions A, B, C and D.
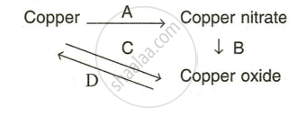
Correct the following, if required:
\[\ce{HNO3}\] is a strong reducing agent.
Correct the following, if required:
\[\ce{NaNO3}\] gives \[\ce{NO2}\] and \[\ce{O2}\] on heating.
Correct the following, if required:
Constant boiling nitric acid contains 80% nitric acid by weight.
Correct the following, if required:
Nitric acid remains colourless even when exposed to light.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE 10 Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid EXERCISE 10 [Pages 170 - 172]
Choose the correct answer:
The nitrate salt which does not give a mixture of \[\ce{NO2}\] and \[\ce{O2}\] on heating is ______.
AgNO3
KNO3
Cu(NO3)2
Zn(NO3)2
The chemical used in the brown ring test is ______.
CuSO4
FeSO4
Fe2(SO4)3
ZnSO4
Lead nitrate decomposes on heating to give ______.
\[\ce{NO}\]
\[\ce{N2O}\]
\[\ce{NO2}\]
N\[\ce{2O5}\]
Name a nitrate of metal which on heating does not give nitrogen dioxide
Name a nitrate which on heating leaves no residue behind.
Name a metal nitrate which on heating is changed into metal oxide.
Name a metal nitrate which on heating is changed into metal.
Name a solution which absorbs nitric oxide.
Name the oxide of nitrogen which turns brown on exposure to air. How is it prepared?
Mention three important uses of nitric acid. Give the property of nitric acid involved in the use.
Explain with the help of a balanced equation, the brown ring test for nitric acid.
why is freshly prepared ferrous sulphate solution used for testing the nitrate radical in the brown ring test?
From the following list of substances, choose one substance in the case which matches the description given below:
Ammonium nitrate, calcium hydrogen carbonate, copper carbonate, lead nitrate, potassium nitrate, sodium carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate, zinc carbonate.
A Substance that gives off only oxygen when heated.
From the following list of substances, choose one substance in the case which matches the description given below:
Ammonium nitrate, calcium hydrogen carbonate, copper carbonate, lead nitrate, potassium nitrate, sodium carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate, zinc carbonate.
A substance which on heating decomposes into dinitrogen oxide [nitrous oxide] and steam.
From the following list of substances, choose one substance in the case which matches the description given below:
Ammonium nitrate, calcium hydrogen carbonate, copper carbonate, lead nitrate, potassium nitrate, sodium carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate, zinc carbonate.
A substance which gives off oxygen and nitrogen dioxide when heated.
From the following list of substances, choose one substance in the case which matches the description given below:
Ammonium nitrate, calcium hydrogen carbonate, copper carbonate, lead nitrate, potassium nitrate, sodium carbonate, sodium hydrogen carbonate, zinc carbonate.
A substance which on heating leaves yellow residue.
The action of heat on the blue crystalline solid X gives a reddish brown gas Y, a gas which re-lights a glowing splint and leaves a black residue. When gas Z, which has a rotten egg smell, is passed through a solution of X, a black ppt. is formed.
- Identify X, Y and Z.
- Write the equation for action of heat on X.
- Write the equation between solution X and gas Z.
X, Y, and Z are three crystalline solids that are soluble in water and have common anion.
To help you to identify X, Y and Z, you are provided with the following experimental observations. Copy and complete the corresponding inferences in (a) to (e).
- A reddish-brown gas is obtained when X, Y, and Z are separately warmed with concentrated sulphuric acid and copper turning added to the mixture.
INFERENCE 1: The common anion is the ______ ion. - When X is heated, it melts and gives off only one gas which re-lights a glowing splint.
INFERENCE 2: The cation in X is either ______ or ______. - The action of heat on Y produces a reddish-brown gas and yellow residue which fuses with a glass of the test tube.
INFERENCE 3: The metal ion present in Y is the ______ ion. - When Z is heated, it leaves no residue. Warming Z with sodium hydroxide solution liberates a gas which turns moist red litmus paper blue.
INFERENCE 4: Z contains the ______ cation. - Write the equations for the following reactions:
- X and concentrated sulphuric acid (below 200°C). (One equation only for either of the cations given in INFERENCE 2)
- The action of heat on Y.
- Concentrated nitric acid is added to copper turnings kept in a beaker.
Dilute nitric acid is generally considered to be a typical acid except for its reaction with metals. In what way is dilute nitric acid different from other acids when it reacts with metals?
Write the equation for the reaction of dilute nitric acid with copper.
Write the equation for the reaction of conc. nitric acid with copper.
Explain why only all-glass apparatus should be used for the preparation of nitric acid by heating concentrated sulphuric acid and potassium nitrate.
Explain why nitric acid is kept in a reagent bottle for a long time.
The figure given below illustrates the apparatus used in the laboratory preparation of nitric acid.
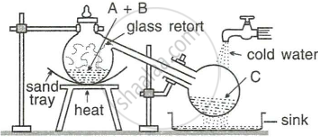
- Name A (a liquid), B (a solid), and C (a liquid). (Do not give the formulae).
- Write an equation to show how nitric acid undergoes decomposition.
- Write the equation for the reaction in which copper is oxidised by concentrated nitric acid.
A dilute acid B does not normally give hydrogen when reacted with metals but does give a gas when reacts with copper. Identify B. Write the equation with copper.
Complete the table:
| Name of Process | Inputs | Equation | Output |
| Ammonia + Air | Nitric acid |
What is the property of nitric acid which allows it to react with copper?
State one observation for the following:
Concentrated nitric acid is reacted with sulphur.
State one observation:
Lead nitrate is heated strongly in a test tube.
Name the gas produced when copper reacts with conc. \[\ce{HNO3}\].
State observation:
Zinc nitrate crystals are strongly heated.
Correct the statement:
Magnesium reacts with nitric acid to liberate hydrogen gas.
Iron is rendered passive with fuming \[\ce{HNO3}\]. Give reason.
Give balanced equation for dilute nitric acid and copper carbonate
Identify the gas evolved when sulphur is treated with concentrated nitric acid \[\ce{NH3}\].
Identify the gas evolved when a few crystals of \[\ce{KNO3}\] are heated in a hard glass test tube
State two relevant observations for lead nitrate crystals heated in a hard glass test tube
Give a balanced equation for the following:
Oxidation of carbon with conc. Nitric acid.
Fill in the blank:
Cold dil. nitric acid reacts with copper to form ______.
hydrogen
nitrogen dioxide
nitric oxide
Give balanced equations for the following:
Laboratory preparation of nitric acid.
Write balanced equations for Action of heat on a mixture of copper and concentrated nitric acid
Identify the acid.
Which is used for the preparation of non-volatile acid.
The acid which is prepared by catalytic oxidation of ammonia.
State one relevant observation for the following:
When crystals of copper nitrate are heated in a test tube.
Explain the following:
Dil. \[\ce{HNO3}\] is generally considered a typical acid but not so in the reaction with metals.
Explain the following:
Concentrated nitric acid appears yellow when it is left standing in a glass bottle.
Explain the following:
An all-glass apparatus is used in the laboratory preparation of nitric acid.
Solutions for 10: Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-10-icse_6:a11ba386c5de4fb5831d789b303b585d.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 10 (Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid are Laboratory Preparation of Nitric Acid, Manufacture of Nitric Acid, Nitric Acid, Physical Properties of Nitric Acid, Chemical Properties of Nitric Acid, Uses of Nitric Acid, Tests for Nitric Acid and Nitrates, Effects of Heat on Nitrates, Laboratory Preparation of Nitric Acid, Manufacture of Nitric Acid, Nitric Acid, Physical Properties of Nitric Acid, Chemical Properties of Nitric Acid, Uses of Nitric Acid, Tests for Nitric Acid and Nitrates, Effects of Heat on Nitrates.
Using Selina Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 10, Study of Compounds C - Nitric Acid Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
