Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A 250 g block slides on a rough horizontal table. Find the work done by the frictional force in bringing the block to rest if it is initially moving at a speed of 40 cm/s. If the friction coefficient between the table and the block is 0⋅1, how far does the block move before coming to rest?
Solution
\[\text{ Given } : \]
\[\text{ Mass of the block, m = 250 gm = 0 . 250 kg } \]
\[\text{ Initial speed of the block, u = 40 cm/s = 0 . 4 m/s } \]
\[\text{ Final speed of the block, }\nu = 0 \]
\[\text{ Coefficient of friction, } \mu = 0 . 1\]
Force in the forward direction is equal to the friction force.
\[\text{ Here } , \mu \text{ R = ma } \]
\[\left( \text{ where a is deceleration } \right)\]
\[a = \left( \frac{\mu R}{m} \right) = \left( \frac{\mu \text{ mg }}{m} \right) = \mu \text{ g } \]
\[ = 0 . 1 \times 9 . 8 = 0 . 98 \text{ m/ s} ^2 \]
\[s = \frac{\nu^2 - u^2}{2a} = 0 . 082 \text{ m } \]
\[ = 8 . 2 \text{ cm } \]
Again, work done against friction,
\[W = - \mu \text{ Rs } \cos \theta\]
\[ = - 1 \times 2 . 5 \times 0 . 082 \times 1\]
\[ = - 0 . 02 J\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = - 0 . 02 J\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A body constrained to move along the z-axis of a coordinate system is subject to a constant force F given by
`F = -hati+2hatj+3hatkN`
Where `hati,hatj,hatk` are unit vectors along the x-, y- and z-axis of the system respectively. What is the work done by this force in moving the body a distance of 4 m along the z-axis ?
A boy is sitting on a chair placed on the floor of a room. Write as many action-reaction pairs of forces as you can.
When you hold a pen and write on your notebook, what kind of force is exerted by you on the pen? By the pen on the notebook? By you on the notebook?
Figure shows a cart. Complete the table shown below.
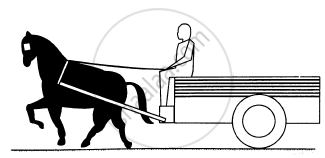
| Force on | Force by | Nature of the Force | Direction |
| Cart |
1 |
||
| Horse |
1 |
||
| Driver |
1 |
When Neils Bohr shook hand with Werner Heisenberg, what kind of force they exerted ?
Which of the following systems may be adequately described by classical physics ?
(a) motion of a cricket ball
(b) motion of a dust particle
(c) a hydrogen atom
(d) a neutron changing to a proton.
Two spherical bodies, each of mass 50 kg, are placed at a separation of 20 cm. Equal charges are placed on the bodies and it is found that the force of Coulomb repulsion equals the gravitational attraction in magnitude. Find the magnitude of the charge placed on either body.
A body builder exerts a force of 150 N against a bullworker and compresses it by 20 cm. Calculate the spring constant of the spring in the bullworker.
The average separation between the proton and the electron in a hydrogen atom in ground state is 5.3 × 10−11 m. (a) Calculate the Coulomb force between them at this separation. (b) When the atom goes into its first excited state the average separation between the proton and the electron increases to four times its value in the ground state. What is the Coulomb force in this state?
In tug of war, the team that exerts a larger tangential force on the ground wins. Consider the period in which a team is dragging the opposite team by applying a larger tangential force on the ground. List which of the following works are positive, which are negative and which are zero?
(a) work by the winning team on the losing team
(b) work by the losing team on the winning team
(c) work by the ground on the winning team
(d) work by the ground on the losing team
(e) total external work on the two teams.
The magnetic force on a charged particle is always perpendicular to its velocity. Can the magnetic force change the velocity of the particles? Speed of the particle?
The work done by all the forces (external and internal) on a system equals the change in ______.
A constant force of 2⋅5 N accelerates a stationary particle of mass 15 g through a displacement of 2⋅5 m. Find the work done and the average power delivered.
A block of mass 2.0 kg is pushed down an inclined plane of inclination 37° with a force of 20 N acting parallel to the incline. It is found that the block moves on the incline with an acceleration of 10 m/s2. If the block started from rest, find the work done (a) by the applied force in the first second, (b) by the weight of the block in the first second and (c) by the frictional force acting on the block in the first second. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Water falling from a 50-m high fall is to be used for generating electric energy. If \[1 \cdot 8 \times {10}^5 \text{ kg } \] of water falls per hour and half the gravitational potential energy can be converted into electrical energy, how many 100 W lamps can be lit with the generated energy?
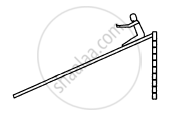
In a children's park, there is a slide which has a total length of 10 m and a height of 8⋅0 m . A vertical ladder is provided to reach the top. A boy weighing 200 N climbs up the ladder to the top of the slide and slides down to the ground. The average friction offered by the slide is three tenth of his weight. Find (a) the work done by the ladder on the boy as he goes up; (b) the work done by the slide on the boy as he comes down. Neglect any work done by forces inside the body of the boy
A uniform chain of mass m and length l overhangs a table with its two third part on the table. Find the work to be done by a person to put the hanging part back on the table.
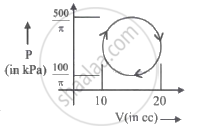
Work done by gas in cyclic process is ______ J.
A cylinder of area 300 cm2 and length 10 cm made of material of specific gravity 0.8 is floated in water with its axis vertical. It is then pushed downward, so as to be just immersed. The work done by the agent who pushes the cylinder into the water is ______ J.
Force acting on a particle is (2`hat"i"` + 3 `hat"j"`) N. Work done by this force is zero, when a particle is moved on the line 3y + kx = 5. Here value of k is ______.
