Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
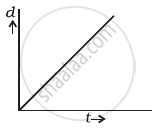
A body is moving unidirectionally under the influence of a source of constant power supplying energy. Which of the diagrams shown in figure correctly shows the displacement-time curve for its motion?
Options
Solution
Explanation:
For constant power
Displacement ∝ t3/2
Because P = `(vecF * dvecs)/(dt) = vecF * vecv` = constant .....(∵ P = constant according to the problem)
Now, will by dimensional analysis
[F][v] = constant
⇒ [MLT–2][LT–1] = constant
⇒ L2T–3 = constant .....(∵ mass is constant)
⇒ L ∝ T3/2
⇒ Displacement (d) ∝ t3/2
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
When you hold a pen and write on your notebook, what kind of force is exerted by you on the pen? By the pen on the notebook? By you on the notebook?
Two charged particles placed at a separation of 20 cm exert 20 N of Coulomb force on each other. What will be the force of the separation is increased to 25 cm?
The force with which the earth attracts an object is called the weight of the object. Calculate the weight of the moon from the following data : The universal constant of gravitation G = 6.67 × 11−11 N−m2/kg2, mass of the moon = 7.36 × 1022 kg, mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and the distance between the earth and the moon = 3.8 × 105 km.
The work done by all the forces (external and internal) on a system equals the change in ______.
A block of weight 100 N is slowly moved up a smooth incline of inclination 37° by a person. Calculate the work done by the person in moving the block through a distance of 2 m, if the driving force is (a) parallel to the incline and (b) in the horizontal direction.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the kinetic energy of the block at the instant the force ceases to act. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A force F = 20 + 10y acts on a particle in y-direction where F is in newton and y in metre. Work done by this force to move the particle from y – 0 to y – 1 m is:
The work done by an applied variable force, F = x + x3 from x = 0 m to x = 2m, where x is displacement, is:
A block of mass 1 kg is pushed up a surface inclined to horizontal at an angle of 30° by a force of 10 N parallel to the inclined surface (Figure). The coefficient of friction between block and the incline is 0.1. If the block is pushed up by 10 m along the incline, calulate
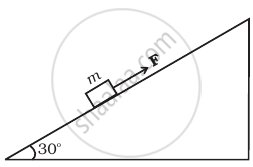
- work done against gravity
- work done against force of friction
- increase in potential energy
- increase in kinetic energy
- work done by applied force.
A cylinder of area 300 cm2 and length 10 cm made of material of specific gravity 0.8 is floated in water with its axis vertical. It is then pushed downward, so as to be just immersed. The work done by the agent who pushes the cylinder into the water is ______ J.