Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The force with which the earth attracts an object is called the weight of the object. Calculate the weight of the moon from the following data : The universal constant of gravitation G = 6.67 × 11−11 N−m2/kg2, mass of the moon = 7.36 × 1022 kg, mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and the distance between the earth and the moon = 3.8 × 105 km.
Solution
The force between the Earth and the Moon is given by \[F = \frac{GMm}{r^2}\]
Here, M is the mass of the earth; m is the mass of the moon and r is the distance between Earth and Moon.
On substituting the values, we get :
\[F = \frac{6 . 67 \times {10}^{- 11} \times 7 . 36 \times {10}^{22} \times 6 \times {10}^{24}}{3 . 8 \times 3 . 8 \times {10}^{16}}\]
\[= \frac{6 . 67 \times 7 . 36 \times {10}^{35}}{(3 . 8 )^2 \times {10}^{16}}\]
\[ = 20 . 3 \times {10}^{19} = 2 . 03 \times {10}^{20} \]
\[ \approx 2 . 0 \times {10}^{20} N\]
∴ The weight of the moon is \[2 . 0 \times {10}^{20} N\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A body of mass m is placed on a table. The earth is pulling the body with a force mg. Taking this force to be the action what is the reaction?
A boy is sitting on a chair placed on the floor of a room. Write as many action-reaction pairs of forces as you can.
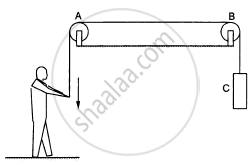
List all the forces acting on (a) the pulley A, (b) the boy and (c) the block C in figure.
Two spherical bodies, each of mass 50 kg, are placed at a separation of 20 cm. Equal charges are placed on the bodies and it is found that the force of Coulomb repulsion equals the gravitational attraction in magnitude. Find the magnitude of the charge placed on either body.
A monkey is sitting on a tree limb. The limb exerts a normal force of 48 N and a frictional force of 20 N. Find the magnitude of the total force exerted by the limb on the monkey.
A body builder exerts a force of 150 N against a bullworker and compresses it by 20 cm. Calculate the spring constant of the spring in the bullworker.
The average separation between the proton and the electron in a hydrogen atom in ground state is 5.3 × 10−11 m. (a) Calculate the Coulomb force between them at this separation. (b) When the atom goes into its first excited state the average separation between the proton and the electron increases to four times its value in the ground state. What is the Coulomb force in this state?
In tug of war, the team that exerts a larger tangential force on the ground wins. Consider the period in which a team is dragging the opposite team by applying a larger tangential force on the ground. List which of the following works are positive, which are negative and which are zero?
(a) work by the winning team on the losing team
(b) work by the losing team on the winning team
(c) work by the ground on the winning team
(d) work by the ground on the losing team
(e) total external work on the two teams.
A block of mass m slides down a smooth vertical circular track. During the motion, the block is in
A constant force of 2⋅5 N accelerates a stationary particle of mass 15 g through a displacement of 2⋅5 m. Find the work done and the average power delivered.
Find the average frictional force needed to stop a car weighing 500 kg at a distance of 25 m if the initial speed is 72 km/h.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the work done by the force of gravity in that one second if the work done by the applied force is 40 J.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the kinetic energy of the block at the instant the force ceases to act. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A block of mass 2.0 kg is pushed down an inclined plane of inclination 37° with a force of 20 N acting parallel to the incline. It is found that the block moves on the incline with an acceleration of 10 m/s2. If the block started from rest, find the work done (a) by the applied force in the first second, (b) by the weight of the block in the first second and (c) by the frictional force acting on the block in the first second. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A block of mass 1 kg is placed at point A of a rough track shown in figure following. If slightly pushed towards right, it stops at point B of the track. Calculate the work done by the frictional force on the block during its transit from A to B.

A force F = 20 + 10y acts on a particle in y-direction where F is in newton and y in metre. Work done by this force to move the particle from y – 0 to y – 1 m is:
A body is moving unidirectionally under the influence of a source of constant power supplying energy. Which of the diagrams shown in figure correctly shows the displacement-time curve for its motion?
A body is being raised to a height h from the surface of earth. What is the sign of work done by gravitational force?
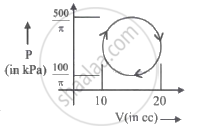
Work done by gas in cyclic process is ______ J.