Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
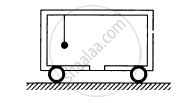
A child sits stationary at one end of a long trolley moving uniformly with a speed V on a smooth horizontal floor. If the child gets up and runs about on the trolley in any manner, what is the speed of the CM of the (trolley + child) system?
Solution 1
The speed of the centre of mass (CM) of a trolley and child system remains unchanged when the child runs around on a moving trolley with uniform speed V on a smooth floor. This is because the child's movements are internal actions within the trolley-child system, and internal forces do not affect the system's total momentum. With no external forces acting on the system, the CM's velocity remains constant at V.
Solution 2
The trolley is moving on a smooth horizontal floor, the smoothness of the floor means that no external horizontal forces are acting on the system. When the child runs on the trolley, the forces exerted by the child on the trolley and by the trolley on the child are both internal forces.
`vec"F"_"ext" = vec0`
According to the law of conservation of momentum,
`"M" vec"v"_"cm" = "constant"`;
`vec"v"_"cm" = "constant"`
This implies that the velocity of the center of mass will remain constant.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A ball kept in a closed box moves in the box making collisions with the walls. The box is kept on a smooth surface. The velocity of the centre of mass
In an elastic collision
In which of the following cases the centre of mass of a rod is certainly not at its centre?
(a) the density continuously increases from left to right
(b) the density continuously decreases from left to right
(c) the density decreases from left to right upto the centre and then increases
(d) the density increases from left to right upto the centre and then decreases.
A car of mass M is at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface and a pendulum bob of mass m hangs from the roof of the cart. The string breaks, the bob falls on the floor, makes serval collisions on the floor and finally lands up in a small slot made in the floor. The horizontal distance between the string and the slot is L. Find the displacement of the cart during this process.
A block of mass 2.0 kg moving 2.0 m/s collides head on with another block of equal mass kept at rest. (a) Find the maximum possible loss in kinetic energy due to the collision. (b) If he actual loss in kinetic energy is half of this maximum, find the coefficient of restitution.
Solve the following problem.
Four uniform solid cubes of edges 10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm are kept on the ground, touching each other in order. Locate centre of mass of their system.
The radius and mass of earth are increased by 0.5%. Which of the following statements are true at the surface of the earth?
A mass of 1kg is suspended by a string. It is first lifted up with an acceleration of 4.9 m/s2 and then lowered down with same acceleration. The ratio of tensions in the string in the two cases, respectively is g = 9.8 m/s2 ______.
Centre of mass is a point ______.
A point charge Q is situated at point B on the ground. A point charge q of mass m is vertically dropped along line AB from a multi-storey building of height h. Find the position of the point charge q when it is in equilibrium.