Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In an elastic collision
Options
the initial kinetic energy is equal to the final kinetic energy
the final kinetic energy is less than the initial kinetic energy
the kinetic energy remains constant
the kinetic energy first increases then decreases.
Solution
the final kinetic energy is less than the initial kinetic energy
As some energy is loss into heat in an inelastic collision, the final kinetic energy is less than the initial kinetic energy.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give the location of the centre of mass of a
- sphere,
- cylinder,
- ring, and
- cube,
each of uniform mass density. Does the centre of mass of a body necessarily lie inside the body?
Consider the following the equations
(A) \[\vec{R} = \frac{1}{M} \sum_i m_i \vec{r_i}\] and
(B) \[\vec{a}_{CM} = \frac{\vec{F}}{M}\]
In a noninertial frame
A nonzero external force acts on a system of particles. The velocity and the acceleration of the centre of mass are found to be v0 and a0 at instant t. It is possible that
(a) v0 = 0, a0 = 0
(b) v0 = 0, a0 ≠ 0
(c) v0 ≠ 0, a0 = 0
(d) v0 ≠ 0, a0 ≠ 0
Two balls are thrown simultaneously in air. The acceleration of the centre of mass of the two balls while in air
Three particles of masses 1.0 kg, 2.0 kg and 3.0 kg are placed at the corners A, B and C respectively of an equilateral triangle ABC of edge 1 m. Locate the centre of mass of the system.
Seven homogeneous bricks, each of length L, are arranged as shown in figure. Each brick is displaced with respect to the one in contact by L/10. Find the x-coordinate fo the centre of mass relative to the origin shown.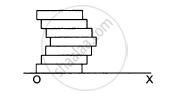
Find the ratio of the linear momenta of two particles of masses 1.0 kg and 4.0 kg if their kinetic energies are equal.
A railroad car of mass M is at rest on frictionless rails when a man of mass m starts moving on the car towards the engine. If the car recoils with a speed v backward on the rails, with what velocity is the man approaching the engine?
A block of mass 2.0 kg moving 2.0 m/s collides head on with another block of equal mass kept at rest. (a) Find the maximum possible loss in kinetic energy due to the collision. (b) If he actual loss in kinetic energy is half of this maximum, find the coefficient of restitution.
Solve the following problem.
A uniform solid sphere of radius R has a hole of radius R/2 drilled inside it. One end of the hole is at the center of the sphere while the other is at the boundary. Locate center of mass of the remaining sphere.
A body of mass 2 kg is acted upon by two forces each of magnitude 1 N and inclined at 60° with each other. The acceleration of the body in m/s is ____________. [cos 60° = 0.5]
A mass of 1kg is suspended by a string. It is first lifted up with an acceleration of 4.9 m/s2 and then lowered down with same acceleration. The ratio of tensions in the string in the two cases, respectively is g = 9.8 m/s2 ______.
A shell of mass 'M' initially at rest suddenly explodes in three fragments. Two of these fragments are of mass 'M/4' each, which move with velocities 3 ms-1 and 4 ms-1 respectively in mutually perpendicular directions. The magnitude of velocity of the third fragment is ______.
For which of the following does the centre of mass lie outside the body?
A uniform square plate has a small piece Q of an irregular shape removed and glued to the centre of the plate leaving a hole behind figure. The CM of the plate is now in the following quadrant of x-y plane ______.
The density of a non-uniform rod of length 1 m is given by ρ(x) = a(1 + bx2) where a and b are constants and 0 ≤ x ≤ 1. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
Figure shows a lamina in x-y plane. Two axes z and z ′ pass perpendicular to its plane. A force F acts in the plane of lamina at point P as shown. Which of the following are true? (The point P is closer to z′-axis than the z-axis.)

- Torque τ caused by F about z axis is along `-hatk`.
- Torque τ′ caused by F about z′ axis is along `-hatk`.
- Torque τ caused by F about z axis is greater in magnitude than that about z axis.
- Total torque is given be τ = τ + τ′.
Find the centre of mass of a uniform (a) half-disc, (b) quarter-disc.
