Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A uniform square plate has a small piece Q of an irregular shape removed and glued to the centre of the plate leaving a hole behind figure. The CM of the plate is now in the following quadrant of x-y plane ______.
Options
I
II
III
IV
Solution
A uniform square plate has a small piece Q of an irregular shape removed and glued to the centre of the plate leaving a hole behind figure. The CM of the plate is now in the following quadrant of x-y plane III.
Explanation:
Consider the adjacent diagram, there is a line shown in the figure drawn along the diagonal. First, the centre of mass of the system was on the dotted line and was shitted towards Q from the centre (Ist quadrant).
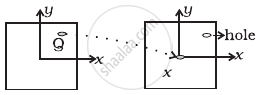
When the mass is removed, it will be on the same line but shifted away from the centre and below (IIIrd quadrant). The position of CM is shown by X in the diagram.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
You are waiting for a train on a railway platform. Your three-year-old niece is standing on your iron trunk containing the luggage. Why does the trunk not recoil as she jumps off on the platform?
You are holding a cage containing a bird. Do you have to make less effort if the bird flies from its position in the cage and manages to stay in the middle without touching the walls of the cage? Does it makes a difference whether the cage is completely closed or it has rods to let air pass?
In an elastic collision
A nonzero external force acts on a system of particles. The velocity and the acceleration of the centre of mass are found to be v0 and a0 at instant t. It is possible that
(a) v0 = 0, a0 = 0
(b) v0 = 0, a0 ≠ 0
(c) v0 ≠ 0, a0 = 0
(d) v0 ≠ 0, a0 ≠ 0
Two balls are thrown simultaneously in air. The acceleration of the centre of mass of the two balls while in air
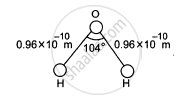
The structure of a water molecule is shown in figure. Find the distance of the centre of mass of the molecule from the centre of the oxygen atom.
In an elastic collision
A block of mass 2.0 kg moving 2.0 m/s collides head on with another block of equal mass kept at rest. (a) Find the maximum possible loss in kinetic energy due to the collision. (b) If he actual loss in kinetic energy is half of this maximum, find the coefficient of restitution.
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose each of the blocks is pulled by a constant force F instead of any impulse. Find the maximum elongation that the spring will suffer and the distance moved by the two blocks in the process.
Centre of mass is a point ______.
