Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
You are holding a cage containing a bird. Do you have to make less effort if the bird flies from its position in the cage and manages to stay in the middle without touching the walls of the cage? Does it makes a difference whether the cage is completely closed or it has rods to let air pass?
Solution
More effort is needed when the cage is closed, while less effort is required when the cage has rods to let the air pass. When a bird flies from its position, it pushes the air downwards. Thus, when the bird is in a cage, the net downward force will be equal to the weight of the cage plus the downward force due to air (the weight of the bird).
However, if the cage has rods to let air pass, the downward force exerted by air become less. Therefore, less effort will be required to hold the cage.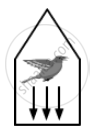
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the HCl molecule, the separation between the nuclei of the two atoms is about 1.27 Å (1 Å = 10–10 m). Find the approximate location of the CM of the molecule, given that a chlorine atom is about 35.5 times as massive as a hydrogen atom and nearly all the mass of an atom is concentrated in its nucleus.
In a head-on collision between two particles, is it necessary that the particles will acquire a common velocity at least for one instant?
A collision experiment is done on a horizontal table kept in an elevator. Do you expect a change in the result if the elevator is accelerated up or down because of the noninertial character of the frame?
A ball kept in a closed box moves in the box making collisions with the walls. The box is kept on a smooth surface. The velocity of the centre of mass
A square plate of edge d and a circular disc of diameter d are placed touching each other at the midpoint of an edge of the plate as shown in figure. Locate the centre of mass of the combination, assuming same mass per unit area for the two plates.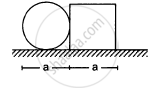
Calculate the velocity of the centre of mass of the system of particles shown in figure.

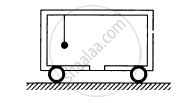
A car of mass M is at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface and a pendulum bob of mass m hangs from the roof of the cart. The string breaks, the bob falls on the floor, makes serval collisions on the floor and finally lands up in a small slot made in the floor. The horizontal distance between the string and the slot is L. Find the displacement of the cart during this process.
A ball of mass m is dropped onto a floor from a certain height. The collision is perfectly elastic and the ball rebounds to the same height and again falls. Find the average force exerted by the ball on the floor during a long time interval.
The axis of rotation of a purely rotating body
(a) must pass through the centre of mass
(b) may pass through the centre of mass
(c) must pass through a particle of the body
(d) may pass through a particle of the body.
Consider a gravity-free hall in which an experimenter of mass 50 kg is resting on a 5 kg pillow, 8 ft above the floor of the hall. He pushes the pillow down so that it starts falling at a speed of 8 ft/s. The pillow makes a perfectly elastic collision with the floor, rebounds and reaches the experimenter's head. Find the time elapsed in the process.
The centre of mass of a system of particles does not depend upon, ______
The centre of mass of a right circular cone of height h, radius R and constant density `sigma` is at ____________.
The radius and mass of earth are increased by 0.5%. Which of the following statements are true at the surface of the earth?
A mass of 1kg is suspended by a string. It is first lifted up with an acceleration of 4.9 m/s2 and then lowered down with same acceleration. The ratio of tensions in the string in the two cases, respectively is g = 9.8 m/s2 ______.
In rotational motion of a rigid body, all particles move with ______.
A uniform square plate has a small piece Q of an irregular shape removed and glued to the centre of the plate leaving a hole behind figure. The CM of the plate is now in the following quadrant of x-y plane ______.
The density of a non-uniform rod of length 1 m is given by ρ(x) = a(1 + bx2) where a and b are constants and 0 ≤ x ≤ 1. The centre of mass of the rod will be at ______.
Figure shows a lamina in x-y plane. Two axes z and z ′ pass perpendicular to its plane. A force F acts in the plane of lamina at point P as shown. Which of the following are true? (The point P is closer to z′-axis than the z-axis.)

- Torque τ caused by F about z axis is along `-hatk`.
- Torque τ′ caused by F about z′ axis is along `-hatk`.
- Torque τ caused by F about z axis is greater in magnitude than that about z axis.
- Total torque is given be τ = τ + τ′.
