Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A copper rod of length 1.0 m is clamped at its middle point. Find the frequencies between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz at which standing longitudinal waves can be set up in the rod. The speed of sound in copper is 3.8 km s−1.
Solution
Given:
Length of copper rod l = 1.0 m
Speed of sound in copper v = 3.8 kms−1 = 3800 m/s
Let f be the frequency of the longitudinal waves.
Wavelength \[\left( \lambda \right)\] will be :
\[\frac{\lambda}{2} = I\]
\[ \Rightarrow \lambda = 2I = 2 \times 1 = 2 \text { m }\]
We know that:
v = fλ
\[\Rightarrow f = \frac{v}{\lambda}\]
So,
\[f = \frac{3800}{2} = 1 . 9 \text { KHz } \]
Therefore, the frequencies between 20 Hz and 20 kHz that will be heard are
= n × 1.9 kHz,
where n = 0, 1, 2, 3, ...10.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
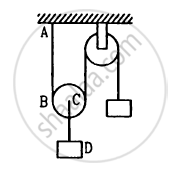
Both the strings, shown in figure, are made of same material and have same cross section. The pulleys are light. The wave speed of a transverse wave in the string AB is
\[\nu_1\] and in CD it is \[\nu_2\]. Then \[\nu_1 / \nu_2\]
Two particles A and B have a phase difference of π when a sine wave passes through the region.
(a) A oscillates at half the frequency of B.
(b) A and B move in opposite directions.
(c) A and B must be separated by half of the wavelength.
(d) The displacements at A and B have equal magnitudes.
The speed of sound in a medium depends on
The speed of sound as measured by a student in the laboratory on a winter day is 340 m s−1 when the room temperature is C17°. What speed will be measured by another student repeating the experiment on a day when the room temperature is 32°C?
Find the change in the volume of 1.0 litre kerosene when it is subjected to an extra pressure of 2.0 × 105 N m−2 from the following data. Density of kerosene = 800 kg m−3and speed of sound in kerosene = 1330 ms−1.
In Quincke's experiment the sound detected is changed from a maximum to a minimum when the sliding tube is moved through a distance of 2.50 cm. Find the frequency of sound if the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1.
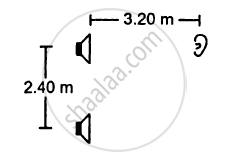
Two stereo speakers are separated by a distance of 2.40 m. A person stands at a distance of 3.20 m directly in front of one of the speakers as shown in figure. Find the frequencies in the audible range (20-2000 Hz) for which the listener will hear a minimum sound intensity. Speed of sound in air = 320 m s−1.
In a resonance column experiment, a tuning fork of frequency 400 Hz is used. The first resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 20.0 cm and the second resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 62.0 cm. (a) Find the speed of sound in air. (b) How much distance above the open end does the pressure node form?
A piston is fitted in a cylindrical tube of small cross section with the other end of the tube open. The tube resonates with a tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz. The piston is gradually pulled out of the tube and it is found that a second resonance occurs when the piston is pulled out through a distance of 32.0 cm. Calculate the speed of sound in the air of the tube.
A 30.0-cm-long wire having a mass of 10.0 g is fixed at the two ends and is vibrated in its fundamental mode. A 50.0-cm-long closed organ pipe, placed with its open end near the wire, is set up into resonance in its fundamental mode by the vibrating wire. Find the tension in the wire. Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A Kundt's tube apparatus has a copper rod of length 1.0 m clamped at 25 cm from one of the ends. The tube contains air in which the speed of sound is 340 m s−1. The powder collects in heaps separated by a distance of 5.0 cm. Find the speed of sound waves in copper.
Calculate the frequency of beats produced in air when two sources of sound are activated, one emitting a wavelength of 32 cm and the other of 32.2 cm. The speed of sound in air is 350 m s−1.
A person riding a car moving at 72 km h−1 sound a whistle emitting a wave of frequency 1250 Hz. What frequency will be heard by another person standing on the road (a) in front of the car (b) behind the car? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
Figure shows a person standing somewhere in between two identical tuning forks. each vibrating at 512 Hz. If both the tuning forks move towards right a speed of 5.5 m s−1, find the number of beats heard by the listener. Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.

A traffic policeman sounds a whistle to stop a car-driver approaching towards him. The car-driver does not stop and takes the plea in court that because of the Doppler shift, the frequency of the whistle reaching him might have gone beyond the audible limit of 25 kHz and he did not hear it. Experiments showed that the whistle emits a sound with frequency closed to 16 kHz. Assuming that the claim of the driver is true, how fast was he driving the car? Take the speed of sound in air to be 330 m s−1. Is this speed practical with today's technology?
A car moving at 108 km h−1 finds another car in front it going in the same direction at 72 km h−1. The first car sounds a horn that has a dominant frequency of 800 Hz. What will be the apparent frequency heard by the driver in the front car? Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
A source emitting sound at frequency 4000 Hz, is moving along the Y-axis with a speed of 22 m s−1. A listener is situated on the ground at the position (660 m, 0). Find the frequency of the sound received by the listener at the instant the source crosses the origin. Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
A source emitting a sound of frequency v is placed at a large distance from an observer. The source starts moving towards the observer with a uniform acceleration a. Find the frequency heard by the observer corresponding to the wave emitted just after the source starts. The speed of sound in the medium is v.
A wave of frequency 500 Hz is traveling with a speed of 350 m/s. (a) What is the phase difference between two displacements at a certain point at times 1.0 ms apart? (b) what will be the smallest distance between two points which are 45° out of phase at an instant of time?
