Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A fair coin is tossed four times, and a person win Re 1 for each head and lose Rs 1.50 for each tail that turns up.
From the sample space calculate how many different amounts of money you can have after four tosses and the probability of having each of these amounts.
Solution
There are five ways in which a head can be obtained in a coin toss. These are as follows.
Total possible outcomes = {HHHH, HHHT, HHTH, HHTT, HTHH, HTHT, HTTH, HTTT, THHH, THHT, THTT, TTHH, TTHT, TTTH, TTTT}
(i) No head is obtained or all four tails are obtained.
Loss on getting all four tails = 4 × 1.50
= Rs. 6
Ways of getting four tails (TTTT) = 1
Total possible outcomes = 16
∴ Probability of getting four tails = `1/16`
(ii) When one head and 3 tails are obtained.
Loss = 3 × 1.50 – 1 × 1
= 4.50 – 1.00
= Rs. 3.50
A head and 3 tails can come up as follows:
{TTTH, TTHT, THTT, HTTT}
∴ A head and 3 tails can come up in 4 ways.
Total possible outcomes = 16
Probability of getting a head = `6/16`
= `1/4`
(iii) When 2 heads and 2 tails appear
Loss = 2 × 1.5 – 1 × 2
= 3 – 2
= Rs. 1
2 heads and 2 tails can come up as follows.
{HHTT, HTHT, HTTH, THHT, THTH, TTHH}
There are six ways in which 2 heads and 2 tails can be obtained.
Total possible outcomes = 16
Probability of getting 2 heads = 2
(iv) When 3 heads and 1 tail appear, then
Profit = 3 × 1 – 1 × 1.5
= 3 – 1.50
= Rs. 1.50
Ways of getting 3 heads = {HHHT, HHHH, HTHH, THHH}
There are four ways in which 3 heads and 1 tail can be obtained.
Total possible outcomes = 16
Probability of getting 3 heads = `4/16`
= `1/4`
(v) All four heads can be obtained in one way, then
Profit = 4 × 1
= Rs. 4
Total possible outcomes = 16
Probability of getting four heads = `4/16`
= `1/4`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which of the following can not be valid assignment of probabilities for outcomes of sample space S = {ω1, ω2,ω3,ω4,ω5,ω6,ω7}
| Assignment | ω1 | ω2 | ω3 | ω4 | ω5 | ω6 | ω7 |
| (a) | 0.1 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| (b) | `1/7` | `1/7` | `1/7` | `1/7` | `1/7` | `1/7` | `1/7` |
| (c) | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
| (d) | –0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | -0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| (e) | `1/14` | `2/14` | `3/14` | `4/14` | `5/14` | `6/14` | `15/14` |
A coin is tossed twice, what is the probability that at least one tail occurs?
A card is selected from a pack of 52 cards.
- How many points are there in the sample space?
- Calculate the probability that the card is an ace of spades.
- Calculate the probability that the card is
- an ace
- black card.
Three coins are tossed once. Find the probability of getting
- 3 heads
- 2 heads
- at least 2 heads
- at most 2 heads
- no head
- 3 tails
- exactly two tails
- no tail
- atmost two tails.
Fill in the blank in following table:
| P(A) | P(B) | P(A ∩ B) | P(A ∪ B) |
| 0.35 | ... | 0.25 | 0.6 |
A box contains 10 red marbles, 20 blue marbles and 30 green marbles. 5 marbles are drawn from the box, what is the probability that all will be blue?
A and B throw a pair of dice. If A throws 9, find B's chance of throwing a higher number.
Two unbiased dice are thrown. Find the probability that the total of the numbers on the dice is greater than 10.
Two unbiased dice are thrown. Find the probability that the sum of the numbers obtained on the two dice is neither a multiple of 2 nor a multiple of 3
If a letter is chosen at random from the English alphabet, find the probability that the letter is a vowel .
If a letter is chosen at random from the English alphabet, find the probability that the letter is a consonant .
In a lottery, a person chooses six different numbers at random from 1 to 20, and if these six numbers match with six number already fixed by the lottery committee, he wins the prize. What is the probability of winning the prize in the game?
Which of the cannot be valid assignment of probability for elementary events or outcomes of sample space S = {w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7}:
| Elementary events: | w1 | w2 | w3 | w4 | w5 | w6 | w7 |
| (ii) |
\[\frac{1}{7}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{7}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{7}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{7}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{7}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{7}\]
|
\[\frac{1}{7}\]
|
Which of the cannot be valid assignment of probability for elementary events or outcomes of sample space S = {w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7}:
| Elementary events: | w1 | w2 | w3 | w4 | w5 | w6 | w7 |
| (iii) | 0.7 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
Which of the cannot be valid assignment of probability for elementary events or outcomes of sample space S = {w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7}:
| Elementary events: | w1 | w2 | w3 | w4 | w5 | w6 | w7 |
| (iv) |
\[\frac{1}{14}\]
|
\[\frac{2}{14}\]
|
\[\frac{3}{14}\]
|
\[\frac{4}{14}\]
|
\[\frac{5}{14}\]
|
\[\frac{6}{14}\]
|
\[\frac{15}{14}\]
|
In a single throw of three dice, find the probability of getting the same number on all the three dice.
A box contains 100 bulbs, 20 of which are defective. 10 bulbs are selected for inspection. Find the probability that: all 10 are defective
A box contains 100 bulbs, 20 of which are defective. 10 bulbs are selected for inspection. Find the probability that all 10 are good
A box contains 100 bulbs, 20 of which are defective. 10 bulbs are selected for inspection. Find the probability that none is defective
An urn contains twenty white slips of paper numbered from 1 through 20, ten red slips of paper numbered from 1 through 10, forty yellow slips of paper numbered from 1 through 40, and ten blue slips of paper numbered from 1 through 10. If these 80 slips of paper are thoroughly shuffled so that each slip has the same probability of being drawn. Find the probabilities of drawing a slip of paper that is numbered 5, 15, 25, or 35
In a leap year the probability of having 53 Sundays or 53 Mondays is ______.
Three squares of chessboard are selected at random. The probability of getting 2 squares of one colour and other of a different colour is ______.
Six new employees, two of whom are married to each other, are to be assigned six desks that are lined up in a row. If the assignment of employees to desks is made randomly, what is the probability that the married couple will have nonadjacent desks?
The accompanying Venn diagram shows three events, A, B, and C, and also the probabilities of the various intersections (for instance, P(A ∩ B) = .07). Determine `P(A ∩ barB)`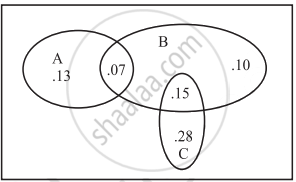
A bag contains 8 red and 5 white balls. Three balls are drawn at random. Find the probability that all the three balls are white
A bag contains 8 red and 5 white balls. Three balls are drawn at random. Find the probability that all one ball is red and two balls are white
If the letters of the word ASSASSINATION are arranged at random. Find the probability that four S’s come consecutively in the word
If the letters of the word ASSASSINATION are arranged at random. Find the probability that two I’s and two N’s come together
While shuffling a pack of 52 playing cards, 2 are accidentally dropped. Find the probability that the missing cards to be of different colours ______.
Seven persons are to be seated in a row. The probability that two particular persons sit next to each other is ______.
6 boys and 6 girls sit in a row at random. The probability that all the girls sit together is ______.
A single letter is selected at random from the word ‘PROBABILITY’. The probability that it is a vowel is ______.
The probability that a person visiting a zoo will see the giraffee is 0.72, the probability that he will see the bears is 0.84 and the probability that he will see both is 0.52.
If A and B are two candidates seeking admission in an engineering College. The probability that A is selected is .5 and the probability that both A and B are selected is at most .3. Is it possible that the probability of B getting selected is 0.7?
The sum of probabilities of two students getting distinction in their final examinations is 1.2
If 4-digit numbers greater than 5,000 are randomly formed from the digits 0, 1, 3, 5, and 7, what is the probability of forming a number divisible by 5 when, the repetition of digits is not allowed?
