Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A horizontal cesium plate (φ = 1.9 eV) is moved vertically downward at a constant speed v in a room full of radiation of wavelength 250 nm and above. What should be the minimum value of v so that the vertically-upward component of velocity is non-positive for each photoelectron?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Solution
Given :-
Work function of the cesium plate, φ = 1.9 eV
Wavelength of radiation, λ = 250 nm
Energy of a photon,
`E = (hc)/lambda`,
where h = Planck's constant
c = speed of light
`therefore E = 1240/250 = 4.96 "eV"`
From Einstein's photoelectric equation, kinetic energy of an electron,
`K = E - phi`
`⇒ K = (hc)/lambda - phi`
[Here , h is Planck's constant and c is the speed of light]
`⇒ K = 4.96 "eV" - 1.9 "eV"`
= 3.06 eV
For non-positive velocity of each photo electron, the velocity of a photoelectron should be equal to minimum velocity of the plate.
∴ Velocity of the photoelectron,
`v = sqrt((2K)/m)` (m = mass of electron)
`therefore v = sqrt((2 xx 3.06 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19)/(9.1 xx 10^-31))`
`= 1.04 xx 10^6 "ms"^-1`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Light of frequency 7.21 × 1014 Hz is incident on a metal surface. Electrons with a maximum speed of 6.0 × 105 m/s are ejected from the surface. What is the threshold frequency for photoemission of electrons?
Is the formula you employ in (a) valid for calculating radius of the path of a 20 MeV electron beam? If not, in what way is it modified?
An electron gun with its collector at a potential of 100 V fires out electrons in a spherical bulb containing hydrogen gas at low pressure (∼10−2 mm of Hg). A magnetic field of 2.83 × 10−4 T curves the path of the electrons in a circular orbit of radius 12.0 cm. (The path can be viewed because the gas ions in the path focus the beam by attracting electrons, and emitting light by electron capture; this method is known as the ‘fine beam tube’ method. Determine e/m from the data.
If light of wavelength 412.5 nm is incident on each of the metals given below, which ones will show photoelectric emission and why?
| Metal | Work Function (eV) |
| Na | 1.92 |
| K | 2.15 |
| Ca | 3.20 |
| Mo | 4.17 |
A photographic film is coated with a silver bromide layer. When light falls on this film, silver bromide molecules dissociate and the film records the light there. A minimum of 0.6 eV is needed to dissociate a silver bromide molecule. Find the maximum wavelength of light that can be recorded by the film.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
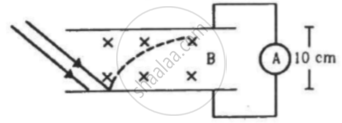
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the emitter and the collector plates are placed at a separation of 10 cm and are connected through an ammeter without any cell. A magnetic field B exists parallel to the plates. The work function of the emitter is 2.39 eV and the light incident on it has wavelengths between 400 nm and 600 nm. Find the minimum value of B for which the current registered by the ammeter is zero. Neglect any effect of space charge.
Plot a graph to show the variation of stopping potential with frequency of incident radiation in relation to photoelectric effect.
Work function of aluminium is 4.2 eV. If two photons each of energy 2.5 eV are incident on its surface, will the emission of electrons take place? Justify your answer.
The stopping potential in an experiment on photoelectric effect is 1.5V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted? Calculate in Joules.
In the case of a photo electric effect experiment, explain the following facts, giving reasons.
The wave theory of light could not explain the existence of the threshold frequency.
In the experimental set up for studying photoelectric effect, if keeping the frequency of the incident radiation and the accelerating potential fixed, the intensity of light is varied, then ______.
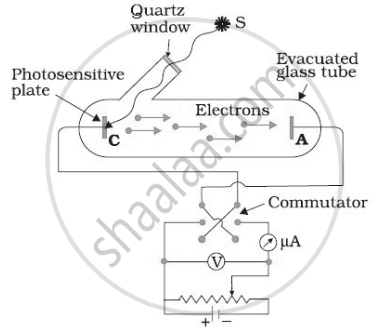
For a given frequency of light and a positive plate potential in the set up below, If the intensity of light is increased then ______.
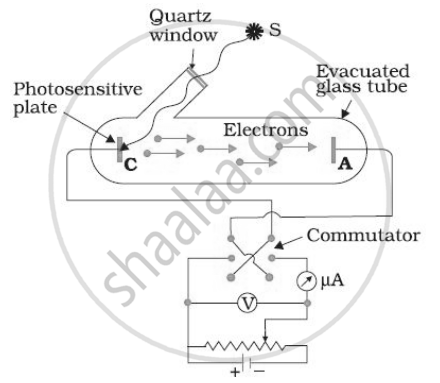
In various experiments on photo electricity, the stopping potential for a given frequency of the incident radiation is ______.
When a beam of 10.6 eV photons of intensity 2.0 W/m2 falls on a platinum surface of area 1.0 × 10-4 m2, only 53% of the incident photons eject photoelectrons. The number of photoelectrons emitted per second is ______.
Cathode rays can be deflected by
