Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A small metal plate (work function φ) is kept at a distance d from a singly-ionised, fixed ion. A monochromatic light beam is incident on the metal plate and photoelectrons are emitted. Find the maximum wavelength of the light beam, so that some of the photoelectrons may go round the ion along a circle.
Solution
From Einstein's photoelectric equation ,
`eV_0 = (hc)/lambda - phi`
⇒ `V_0 = ((hc)/lambda - phi)1/e`
Here, V0 = stopping potential
h = Planck's constant
c = speed of light
`phi ` = work function
The particle will move in a circle when the stopping potential is equal to the potential due to the singly charged ion at that point so that the particle gets the required centripetal force for its circular motion.
`⇒ (Ke)/(2d) = ((hc)/lambda - phi)1/e`
`⇒ (Ke^2)/(2d) = (hc)/lambda - phi`
`⇒ (hc)/lambda = (Ke^2)/(2d) + phi = (Ke^2+2dphi)/(2d)`
`⇒ lambda = ((hc)(2d))/(ke^2+2dphi)`
`⇒ lambda = (2hdc)/(1/(4pi∈_0)e^2+2dphi`
`⇒ lambda = (8pi∈_0hcd)/(e^2+8pi∈_0dphi)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In an experiment on the photoelectric effect, the slope of the cut-off voltage versus the frequency of incident light is found to be 4.12 × 10−15 Vs. Calculate the value of Planck’s constant.
Light of wavelength 488 nm is produced by an argon laser which is used in the photoelectric effect. When light from this spectral line is incident on the emitter, the stopping (cut-off) potential of photoelectrons is 0.38 V. Find the work function of the material from which the emitter is made.
Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation?
point out any two characteristic properties of photons on which Einstein’s photoelectric equation is based ?
Define the terms (i) ‘cut-off voltage’ and (ii) ‘threshold frequency’ in relation to the phenomenon of photoelectric effect.
Using Einstein’s photoelectric equation shows how the cut-off voltage and threshold frequency for a given photosensitive material can be determined with the help of a suitable plot/graph.
A non-monochromatic light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect. The stopping potential
The electric field at a point associated with a light wave is `E = (100 "Vm"^-1) sin [(3.0 xx 10^15 "s"^-1)t] sin [(6.0 xx 10^15 "s"^-1)t]`.If this light falls on a metal surface with a work function of 2.0 eV, what will be the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Consider the faster electron emitted parallel to the large metal plate. Find the displacement of this electron parallel to its initial velocity before it strikes the large metal plate.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Use Einstein's photoelectric equation to show how from this graph,
(i) Threshold frequency, and
(ii) Planck's constant can be determined.
According to Einstein's photoelectric equation, the plot of the kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons from a metal versus the frequency of the incident radiation gives a straight line, whose slope ______.
Each photon has the same speed but different ______.
The wavelength of a photon needed to remove a proton from a nucleus which is bound to the nucleus with 1 MeV energy is nearly ______.
There are materials which absorb photons of shorter wavelength and emit photons of longer wavelength. Can there be stable substances which absorb photons of larger wavelength and emit light of shorter wavelength.
A student performs an experiment on photoelectric effect, using two materials A and B. A plot of Vstop vs ν is given in Figure.
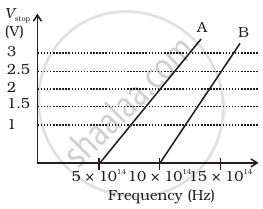
- Which material A or B has a higher work function?
- Given the electric charge of an electron = 1.6 × 10–19 C, find the value of h obtained from the experiment for both A and B.
Comment on whether it is consistent with Einstein’s theory:
Radiation of frequency 1015 Hz is incident on three photosensitive surfaces A, B and C. Following observations are recorded:
Surface A: no photoemission occurs
Surface B: photoemission occurs but the photoelectrons have zero kinetic energy.
Surface C: photo emission occurs and photoelectrons have some kinetic energy.
Using Einstein’s photo-electric equation, explain the three observations.
A photon of wavelength 663 nm is incident on a metal surface. The work function of the metal is 1.50 eV. The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is ______.
The photon emitted during the de-excitation from the first excited level to the ground state of a hydrogen atom is used to irradiate a photocathode in which the stopping potential is 5 V. Calculate the work function of the cathode used.
