Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the positive X-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is, ______
Options
zero
increasing with x
decreasing with x
remaining constant
Solution
A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the positive X-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is, remaining constant.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A heavy particle of mass m falls freely near the earth's surface. What is the torque acting on this particle about a point 50 cm east to the line of motion? Does this torque produce any angular acceleration in the particle?
If the resultant torque of all the forces acting on a body is zero about a point, is it necessary that it will be zero about any other point?
A simple pendulum of length l is pulled aside to make an angle θ with the vertical. Find the magnitude of the torque of the weight ω of the bob about the point of suspension. When is the torque zero?
Define torque and mention its unit.
A Merry-go-round, made of a ring-like platform of radius R and mass M, is revolving with angular speed ω. A person of mass M is standing on it. At one instant, the person jumps off the round, radially away from the centre of the round (as seen from the round). The speed of the round afterwards is ______.
The net external torque on a system of particles about an axis is zero. Which of the following are compatible with it?
- The forces may be acting radially from a point on the axis.
- The forces may be acting on the axis of rotation.
- The forces may be acting parallel to the axis of rotation.
- The torque caused by some forces may be equal and opposite to that caused by other forces.
A uniform cube of mass m and side a is placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. A vertical force F is applied to the edge as shown in figure. Match the following (most appropriate choice):
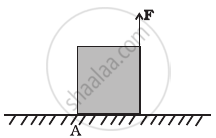
| (a) mg/4 < F < mg/2 | (i) Cube will move up. |
| (b) F > mg/2 | (ii) Cube will not exhibit motion. |
| (c) F > mg | (iii) Cube will begin to rotate and slip at A. |
| (d) F = mg/4 | (iv) Normal reaction effectively at a/3 from A, no motion. |
A uniform sphere of mass m and radius R is placed on a rough horizontal surface (Figure). The sphere is struck horizontally at a height h from the floor. Match the following:
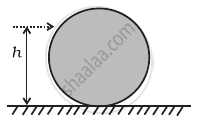
| Column I | Column II | |
| (a) h = R/2 | (i) | Sphere rolls without slipping with a constant velocity and no loss of energy. |
| (b) h = R | (ii) | Sphere spins clockwise, loses energy by friction. |
| (c) h = 3R/2 | (iii) | Sphere spins anti-clockwise, loses energy by friction. |
| (d) h = 7R/5 | (iv) | Sphere has only a translational motion, looses energy by friction. |
A particle of mass 'm' is moving in time 't' on a trajectory given by
`vecr = 10alphat^2hati + 5beta(t - 5)hatj`
Where α and β are dimensional constants.
The angular momentum of the particle becomes the same as it was for t = 0 at time t = ______ seconds.
The magnitude of the torque on a particle of mass 1 kg is 2.5 Nm about the origin. If the force acting on it is 1 N, and the distance of the particle from the origin is 5 m, the angle between the force and the position vector is (in radians) ______.
