Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the positive X-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is, ______
पर्याय
zero
increasing with x
decreasing with x
remaining constant
उत्तर
A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the positive X-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is, remaining constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the components along the x, y, z axes of the angular momentum l of a particle, whose position vector is r with components x, y, z and momentum is p with components px, py and 'p_z`. Show that if the particle moves only in the x-y plane the angular momentum has only a z-component.
The torque of the weight of any body about any vertical axis is zero. If it always correct?
The torque of a force \[\overrightarrow F \] about a point is defined as \[\overrightarrow\Gamma = \overrightarrow r \times \overrightarrow F.\] Suppose \[\overrightarrow r, \overrightarrow F\] and \[\overrightarrow \Gamma\] are all nonzero. Is \[r \times \overrightarrow\Gamma || \overrightarrow F\] always true? Is it ever true?
When a body is weighed on an ordinary balance we demand that the arum should be horizontal if the weights on the two pans are equal. Suppose equal weights are put on the two pans, the arm is kept at an angle with the horizontal and released. Is the torque of the two weights about the middle point (point of support) zero? Is the total torque zero? If so, why does the arm rotate and finally become horizontal?
Equal torques act on the disc A and B of the previous problem, initially both being at rest. At a later instant, the linear speeds of a point on the rim of A and another point on the rim of B are \[\nu_A\] and \[\nu_B\] respectively. We have
When a force of 6⋅0 N is exerted at 30° to a wrench at a distance of 8 cm from the nut it is just able to loosen the nut. What force F would be sufficient to loosen it if it acts perpendicularly to the wrench at 16 cm from the nut?

A rope is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N?
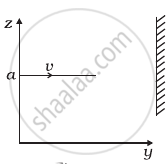
A particle of mass m is moving in yz-plane with a uniform velocity v with its trajectory running parallel to + ve y-axis and intersecting z-axis at z = a (Figure). The change in its angular momentum about the origin as it bounces elastically from a wall at y = constant is ______.
Two discs of moments of inertia I1 and I2 about their respective axes (normal to the disc and passing through the centre), and rotating with angular speed ω2 and ω2 are brought into contact face to face with their axes of rotation coincident.
- Does the law of conservation of angular momentum apply to the situation? why?
- Find the angular speed of the two-disc system.
- Calculate the loss in kinetic energy of the system in the process.
- Account for this loss.
The position vector of 1 kg object is `vecr = (3hati - hatj)` m and its velocity `vecv = (3hati + hatk)` ms-1. The magnitude of its angular momentum is `sqrtx` Nm where x is ______.
