Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A rope is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N?
पर्याय
0.25 rad s–2
25 rad s–2
5 m s–2
25 m s–2
उत्तर
25 rad s–2
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The torque of the weight of any body about any vertical axis is zero. If it always correct?
The torque of a force \[\overrightarrow F \] about a point is defined as \[\overrightarrow\Gamma = \overrightarrow r \times \overrightarrow F.\] Suppose \[\overrightarrow r, \overrightarrow F\] and \[\overrightarrow \Gamma\] are all nonzero. Is \[r \times \overrightarrow\Gamma || \overrightarrow F\] always true? Is it ever true?
A heavy particle of mass m falls freely near the earth's surface. What is the torque acting on this particle about a point 50 cm east to the line of motion? Does this torque produce any angular acceleration in the particle?
A body is in translational equilibrium under the action of coplanar forces. If the torque of these forces is zero about a point, is it necessary that it will also be zero about any other point?
A 6⋅5 m long ladder rests against a vertical wall reaching a height of 6⋅0 m. A 60 kg man stands half way up the ladder.
- Find the torque of the force exerted by the man on the ladder about the upper end of the ladder.
- Assuming the weight of the ladder to be negligible as compared to the man and assuming the wall to be smooth, find the force exerted by the ground on the ladder.
Choose the correct alternatives:
- For a general rotational motion, angular momentum L and angular velocity ω need not be parallel.
- For a rotational motion about a fixed axis, angular momentum L and angular velocity ω are always parallel.
- For a general translational motion , momentum p and velocity v are always parallel.
- For a general translational motion, acceleration a and velocity v are always parallel.
Figure shows two identical particles 1 and 2, each of mass m, moving in opposite directions with same speed v along parallel lines. At a particular instant, r1 and r2 are their respective position vectors drawn from point A which is in the plane of the parallel lines. Choose the correct options:
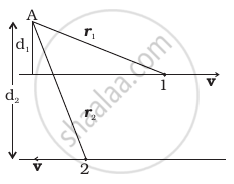
- Angular momentum l1 of particle 1 about A is l1 = mvd1
- Angular momentum l2 of particle 2 about A is l2 = mvr2
- Total angular momentum of the system about A is l = mv(r1 + r2)
- Total angular momentum of the system about A is l = mv (d2 − d1)
⊗ represents a unit vector coming out of the page.
⊗ represents a unit vector going into the page.
The net external torque on a system of particles about an axis is zero. Which of the following are compatible with it?
- The forces may be acting radially from a point on the axis.
- The forces may be acting on the axis of rotation.
- The forces may be acting parallel to the axis of rotation.
- The torque caused by some forces may be equal and opposite to that caused by other forces.
The position vector of 1 kg object is `vecr = (3hati - hatj)` m and its velocity `vecv = (3hati + hatk)` ms-1. The magnitude of its angular momentum is `sqrtx` Nm where x is ______.
Angular momentum of a single particle moving with constant speed along the circular path ______.
