Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A rope is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N?
विकल्प
0.25 rad s–2
25 rad s–2
5 m s–2
25 m s–2
उत्तर
25 rad s–2
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The torque of the weight of any body about any vertical axis is zero. If it always correct?
Equal torques act on the disc A and B of the previous problem, initially both being at rest. At a later instant, the linear speeds of a point on the rim of A and another point on the rim of B are \[\nu_A\] and \[\nu_B\] respectively. We have
Calculate the total torque acting on the body shown in the following figure about the point O.

Two discs of the same moment of inertia rotating about their regular axis passing through centre and perpendicular to the plane of the disc with angular velocities ω1 and ω2. They are brought in to contact face to face coinciding with the axis of rotation. The expression for loss of energy during this process is, ______
Define torque and mention its unit.
What are the conditions in which force can not produce torque?
The net external torque on a system of particles about an axis is zero. Which of the following are compatible with it?
- The forces may be acting radially from a point on the axis.
- The forces may be acting on the axis of rotation.
- The forces may be acting parallel to the axis of rotation.
- The torque caused by some forces may be equal and opposite to that caused by other forces.
Two discs of moments of inertia I1 and I2 about their respective axes (normal to the disc and passing through the centre), and rotating with angular speed ω2 and ω2 are brought into contact face to face with their axes of rotation coincident.
- Does the law of conservation of angular momentum apply to the situation? why?
- Find the angular speed of the two-disc system.
- Calculate the loss in kinetic energy of the system in the process.
- Account for this loss.
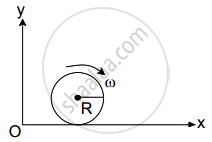
A spherical shell of 1 kg mass and radius R is rolling with angular speed ω on horizontal plane (as shown in figure). The magnitude of angular momentum of the shell about the origin O is `a/3 R^2` ω. The value of a will be:
A rod of mass 'm' hinged at one end is free to rotate in a horizontal plane. A small bullet of mass m/4 travelling with speed 'u' hits the rod and attaches to it at its centre. Find the angular speed of rotation of rod just after the bullet hits the rod 3. [take length of the rod as 'l']
