Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The net external torque on a system of particles about an axis is zero. Which of the following are compatible with it?
- The forces may be acting radially from a point on the axis.
- The forces may be acting on the axis of rotation.
- The forces may be acting parallel to the axis of rotation.
- The torque caused by some forces may be equal and opposite to that caused by other forces.
उत्तर
a, b, c and d
Explanation:
We know that torque on a system of particles `τ = r xx F = F sin θ hatn)` ......(i)
Where, θ is the angle between r and F, and `hatn` is a unit vector perpendicular to both r and F.
- When forces act radially, θ = 0 hence |τ| = 0 .....[From equation (i)]
- When forces are acting on the axis of rotation, r = 0, |τ| = 0 ......[From equation (i)]
- When forces acting parallel to the axis of rotation θ = 0°, |τ| = 0 .....[From equation (i)]
- When torque by forces are equal and opposite, the, τnet = τ1 = τ2 = 0
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If several forces act on a particle, the total torque on the particle may be obtained by first finding the resultant force and then taking torque of this resultant. Prove this. Is this result valid for the forces acting on different particles of a body in such a way that their lines of action intersect at a common point?
A cubical block of mass m and edge a slides down a rough inclined plane of inclination θ with a uniform speed. Find the torque of the normal force acting on the block about its centre.
A 6⋅5 m long ladder rests against a vertical wall reaching a height of 6⋅0 m. A 60 kg man stands half way up the ladder.
- Find the torque of the force exerted by the man on the ladder about the upper end of the ladder.
- Assuming the weight of the ladder to be negligible as compared to the man and assuming the wall to be smooth, find the force exerted by the ground on the ladder.
A rope is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N?
The ratio of the acceleration for a solid sphere (mass m and radius R) rolling down an incline of angle θ without slipping and slipping down the incline without rolling is, ______
A particle of mass 5 units is moving with a uniform speed of v = `3sqrt 2` units in the XOY plane along the line y = x + 4. Find the magnitude of angular momentum
Figure shows two identical particles 1 and 2, each of mass m, moving in opposite directions with same speed v along parallel lines. At a particular instant, r1 and r2 are their respective position vectors drawn from point A which is in the plane of the parallel lines. Choose the correct options:
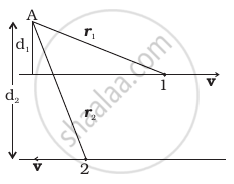
- Angular momentum l1 of particle 1 about A is l1 = mvd1
- Angular momentum l2 of particle 2 about A is l2 = mvr2
- Total angular momentum of the system about A is l = mv(r1 + r2)
- Total angular momentum of the system about A is l = mv (d2 − d1)
⊗ represents a unit vector coming out of the page.
⊗ represents a unit vector going into the page.
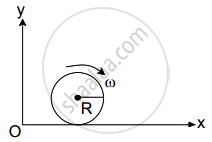
A spherical shell of 1 kg mass and radius R is rolling with angular speed ω on horizontal plane (as shown in figure). The magnitude of angular momentum of the shell about the origin O is `a/3 R^2` ω. The value of a will be:
A rod of mass 'm' hinged at one end is free to rotate in a horizontal plane. A small bullet of mass m/4 travelling with speed 'u' hits the rod and attaches to it at its centre. Find the angular speed of rotation of rod just after the bullet hits the rod 3. [take length of the rod as 'l']
A particle of mass 'm' is moving in time 't' on a trajectory given by
`vecr = 10alphat^2hati + 5beta(t - 5)hatj`
Where α and β are dimensional constants.
The angular momentum of the particle becomes the same as it was for t = 0 at time t = ______ seconds.
