Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A particle of mass 5 units is moving with a uniform speed of v = `3sqrt 2` units in the XOY plane along the line y = x + 4. Find the magnitude of angular momentum
उत्तर
Given,
Mass = 5 units
Speed = v = `3sqrt 2` units
Y = X + 4
Angular momentum = L = m`(overliner xx overlinev)`
= `m(Xhati + yhatj) xx (vhati + vhatj) = m[xvhatk - vyhatk] = m[xvhatk - v(x + 4)hatk]`
L = `-mvhatk = -4 xx 5 xx 3sqrt2hatk = -60sqrt2hatk`
L = `60sqrt2` units.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a body is weighed on an ordinary balance we demand that the arum should be horizontal if the weights on the two pans are equal. Suppose equal weights are put on the two pans, the arm is kept at an angle with the horizontal and released. Is the torque of the two weights about the middle point (point of support) zero? Is the total torque zero? If so, why does the arm rotate and finally become horizontal?
The density of a rod gradually decreases from one end to the other. It is pivoted at an end so that it can move about a vertical axis though the pivot. A horizontal force F is applied on the free end in a direction perpendicular to the rod. The quantities, that do not depend on which end of the rod is pivoted, are ________________ .
A simple pendulum of length l is pulled aside to make an angle θ with the vertical. Find the magnitude of the torque of the weight ω of the bob about the point of suspension. When is the torque zero?
Calculate the total torque acting on the body shown in the following figure about the point O.

A cubical block of mass m and edge a slides down a rough inclined plane of inclination θ with a uniform speed. Find the torque of the normal force acting on the block about its centre.
What are the conditions in which force can not produce torque?
The net external torque on a system of particles about an axis is zero. Which of the following are compatible with it?
- The forces may be acting radially from a point on the axis.
- The forces may be acting on the axis of rotation.
- The forces may be acting parallel to the axis of rotation.
- The torque caused by some forces may be equal and opposite to that caused by other forces.
A uniform cube of mass m and side a is placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. A vertical force F is applied to the edge as shown in figure. Match the following (most appropriate choice):
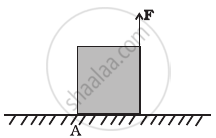
| (a) mg/4 < F < mg/2 | (i) Cube will move up. |
| (b) F > mg/2 | (ii) Cube will not exhibit motion. |
| (c) F > mg | (iii) Cube will begin to rotate and slip at A. |
| (d) F = mg/4 | (iv) Normal reaction effectively at a/3 from A, no motion. |
A rod of mass 'm' hinged at one end is free to rotate in a horizontal plane. A small bullet of mass m/4 travelling with speed 'u' hits the rod and attaches to it at its centre. Find the angular speed of rotation of rod just after the bullet hits the rod 3. [take length of the rod as 'l']
The position vector of 1 kg object is `vecr = (3hati - hatj)` m and its velocity `vecv = (3hati + hatk)` ms-1. The magnitude of its angular momentum is `sqrtx` Nm where x is ______.
