Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
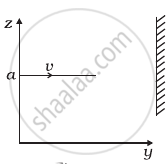
A particle of mass m is moving in yz-plane with a uniform velocity v with its trajectory running parallel to + ve y-axis and intersecting z-axis at z = a (Figure). The change in its angular momentum about the origin as it bounces elastically from a wall at y = constant is ______.
Options
`mva hate_x`
`2mva hate_x`
`ymv hate_x`
`2ymv hate_x`
Solution
A particle of mass m is moving in yz-plane with a uniform velocity v with its trajectory running parallel to + ve y-axis and intersecting z-axis at z = a (Figure). The change in its angular momentum about the origin as it bounces elastically from a wall at y = constant is `underline(2mva hate_x)`.
Explanation:
The initial velocity is `vhati = vhate_y` and, after reflection from the wall, the final velocity is `v_f = - vhate_y`. The trajectory is described as `r = yhate_y + ahate_z`. Hence the change in angular momentum is `r xx m(v_f - v_i) = 2mvahate_x`.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the components along the x, y, z axes of the angular momentum l of a particle, whose position vector is r with components x, y, z and momentum is p with components px, py and 'p_z`. Show that if the particle moves only in the x-y plane the angular momentum has only a z-component.
A rectangular brick is kept on a table with a part of its length projecting out. It remains at rest if the length projected is slightly less than half the total length but it falls down if the length projected is slightly more than half the total length. Give reason.
When a body is weighed on an ordinary balance we demand that the arum should be horizontal if the weights on the two pans are equal. Suppose equal weights are put on the two pans, the arm is kept at an angle with the horizontal and released. Is the torque of the two weights about the middle point (point of support) zero? Is the total torque zero? If so, why does the arm rotate and finally become horizontal?
When a force of 6⋅0 N is exerted at 30° to a wrench at a distance of 8 cm from the nut it is just able to loosen the nut. What force F would be sufficient to loosen it if it acts perpendicularly to the wrench at 16 cm from the nut?

Calculate the total torque acting on the body shown in the following figure about the point O.

A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to the positive X-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is, ______
What are the conditions in which force can not produce torque?
Choose the correct alternatives:
- For a general rotational motion, angular momentum L and angular velocity ω need not be parallel.
- For a rotational motion about a fixed axis, angular momentum L and angular velocity ω are always parallel.
- For a general translational motion , momentum p and velocity v are always parallel.
- For a general translational motion, acceleration a and velocity v are always parallel.
Figure shows two identical particles 1 and 2, each of mass m, moving in opposite directions with same speed v along parallel lines. At a particular instant, r1 and r2 are their respective position vectors drawn from point A which is in the plane of the parallel lines. Choose the correct options:
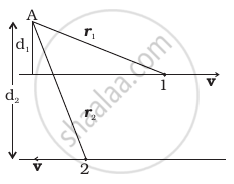
- Angular momentum l1 of particle 1 about A is l1 = mvd1
- Angular momentum l2 of particle 2 about A is l2 = mvr2
- Total angular momentum of the system about A is l = mv(r1 + r2)
- Total angular momentum of the system about A is l = mv (d2 − d1)
⊗ represents a unit vector coming out of the page.
⊗ represents a unit vector going into the page.
A solid sphere is rotating in free space. If the radius of the sphere is increased while keeping the mass the same, which one of the following will not be affected?
