Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A plot of volume (V) versus temperature (T) for a gas at constant pressure is a straight line passing through the origin. The plots at different values of pressure are shown in Figure. Which of the following order of pressure is correct for this gas?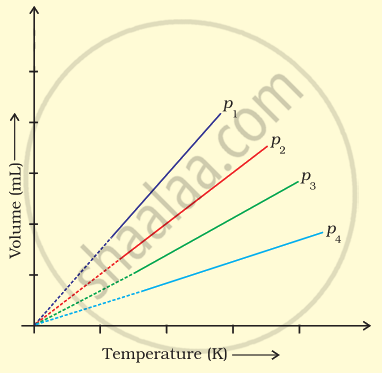
Options
p1 > p2 > p3 > p4
p1 = p2 = p3 = p4
p1 < p2 < p3 < p4
p1 < p2 = p3 < p4
Solution
p1 < p2 < p3 < p4
Explanation:
t a particular temperature, PV is constant
Therefore, `V oo 1/p`
So, as v1 > v2 > v3 > v4 the order of pressure: p1 < p2 < p3 < p4 .
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which of the following is the correct expression for the equation of state of van der Waals gas?
Compressibility factor for CO2 at 400 K and 71.0 bar is 0.8697. The molar volume of CO2 under these conditions is
Suppose there is a tiny sticky area on the wall of a container of gas. Molecules hitting this area stick there permanently. Is the pressure greater or less than on the ordinary area of walls?
Write the Van der Waals equation for a real gas. Explain the correction term for pressure and volume.
Under which of the following two conditions applied together, a gas deviates most from the ideal behaviour?
(i) Low pressure
(ii) High pressure
(iii) Low temperature
(iv) High temperature
Value of universal gas constant (R) is same for all gases. What is its physical significance?
Compressibility factor, Z, of a gas is given as Z = `(pV)/(nRT)`. What is the value of Z for an ideal gas?
Assertion (A): At constant temperature, pV vs V plot for real gases is not a straight line.
Reason (R): At high pressure all gases have \[\ce{Z}\] > 1 but at intermediate pressure most gases have \[\ce{Z}\] < 1.
In van der Waal's equation for the real gas, the expression for the net force of attraction amongst the gas molecules is given by:
Choose the correct option for the total pressure (in atm.) in a mixture of 4g \[\ce{O2}\] and 2g \[\ce{H2}\] confined in a total volume of one litre at 0°C is ______.
[Given R = 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1, T = 273 K]
