Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Compressibility factor, Z, of a gas is given as Z = `(pV)/(nRT)`. What is the value of Z for an ideal gas?
Solution
The value of Z for an ideal gas is 1.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In what way real gases differ from ideal gases.
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if it is compressed to a smaller volume at a constant temperature.
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if the temperature is raised while keeping the volume constant.
Write the Van der Waals equation for a real gas. Explain the correction term for pressure and volume.
A plot of volume (V) versus temperature (T) for a gas at constant pressure is a straight line passing through the origin. The plots at different values of pressure are shown in Figure. Which of the following order of pressure is correct for this gas?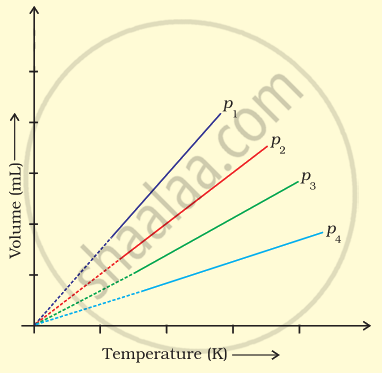
Under which of the following two conditions applied together, a gas deviates most from the ideal behaviour?
(i) Low pressure
(ii) High pressure
(iii) Low temperature
(iv) High temperature
Value of universal gas constant (R) is same for all gases. What is its physical significance?
Match the following graphs of ideal gas with their co-ordinates:
| Graphical representation | x and y co-ordinates |
(i)  |
(a) pV vs. V |
(ii) 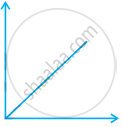 |
(b) p vs. V |
(iii) 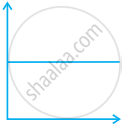 |
(c) p vs. `1/V` |
Assertion (A): At constant temperature, pV vs V plot for real gases is not a straight line.
Reason (R): At high pressure all gases have \[\ce{Z}\] > 1 but at intermediate pressure most gases have \[\ce{Z}\] < 1.
Choose the correct option for the total pressure (in atm.) in a mixture of 4g \[\ce{O2}\] and 2g \[\ce{H2}\] confined in a total volume of one litre at 0°C is ______.
[Given R = 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1, T = 273 K]
