Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Value of universal gas constant (R) is same for all gases. What is its physical significance?
Solution
Unit of R depends on the units of p, V and T are measured, We know, `R = (pV)/(nT)`
Now, let's say, the pressure is measured in Pascal, per mole volume is measured in m3 and temperature is measured in Kelvin, then. Units of ‘R’ are Pa m3K–1 mol–1. Also, R is work done per mole per kelvin. It’s unit is J K–1 mol–1 (Joule is the unit of work done).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Calculate the volume occupied by 8.8 g of CO2 at 31.1°C and 1 bar pressure. R = 0.083 bar L K–1 mol–1.
Compressibility factor for CO2 at 400 K and 71.0 bar is 0.8697. The molar volume of CO2 under these conditions is
Maximum deviation from ideal gas is expected from
Can a Van der Waals gas with a = 0 be liquefied? explain.
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if the temperature is raised while keeping the volume constant.
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if more gas is introduced into the same volume and at the same temperature.
Write the Van der Waals equation for a real gas. Explain the correction term for pressure and volume.
Match the following graphs of ideal gas with their co-ordinates:
| Graphical representation | x and y co-ordinates |
(i)  |
(a) pV vs. V |
(ii) 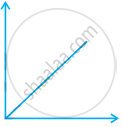 |
(b) p vs. V |
(iii) 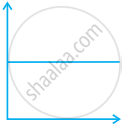 |
(c) p vs. `1/V` |
Assertion (A): At constant temperature, pV vs V plot for real gases is not a straight line.
Reason (R): At high pressure all gases have \[\ce{Z}\] > 1 but at intermediate pressure most gases have \[\ce{Z}\] < 1.
In van der Waal's equation for the real gas, the expression for the net force of attraction amongst the gas molecules is given by:
