Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Suppose there is a tiny sticky area on the wall of a container of gas. Molecules hitting this area stick there permanently. Is the pressure greater or less than on the ordinary area of walls?
Solution
- Molecules hitting the tiny sticky area on the wall of the container of gas moves faster as they get closer to the adhesive surface, but this effect is not permanent.
- The pressure on the sticky wall is greater than on the ordinary area of walls.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Calculate the volume occupied by 8.8 g of CO2 at 31.1°C and 1 bar pressure. R = 0.083 bar L K–1 mol–1.
25 g of each of the following gases are taken at 27°C and 600 mm Hg pressure. Which of these will have the least volume?
In what way real gases differ from ideal gases.
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if more gas is introduced into the same volume and at the same temperature.
Which of the following gases would you expect to deviate from ideal behavior under conditions of low-temperature F2, Cl2, or Br2? Explain.
A plot of volume (V) versus temperature (T) for a gas at constant pressure is a straight line passing through the origin. The plots at different values of pressure are shown in Figure. Which of the following order of pressure is correct for this gas?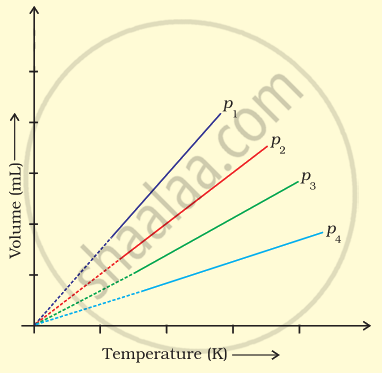
If 1 gram of each of the following gases are taken at STP, which of the gases will occupy (a) greatest volume and (b) smallest volume?
\[\ce{CO, H2O, CH4 , NO}\]
Isotherms of carbon dioxide gas are shown in figure. Mark a path for changing gas into liquid such that only one phase (i.e., either a gas or a liquid) exists at any time during the change. Explain how the temperature, volume and pressure should be changed to carry out the change.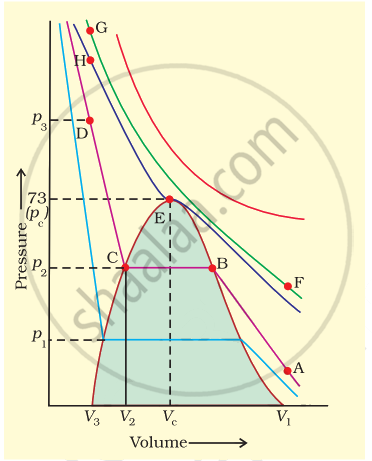
In van der Waal's equation for the real gas, the expression for the net force of attraction amongst the gas molecules is given by:
Choose the correct option for the total pressure (in atm.) in a mixture of 4g \[\ce{O2}\] and 2g \[\ce{H2}\] confined in a total volume of one litre at 0°C is ______.
[Given R = 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1, T = 273 K]
