Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
3: Periodic Classification Of Elements
4: Hydrogen
5: Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals
▶ 6: Gaseous State
7: Thermodynamics
8: Physical and Chemical Equilibrium
9: Solutions
10: Chemical bonding
11: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
12: Basic concept of organic reactions
13: Hydrocarbons
14: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
15: Environmental Chemistry
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 6 - Gaseous State Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 6 - Gaseous State - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: Gaseous State
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board 6 Gaseous State Evaluation [Pages 178 - 183]
Choose the best answer
Gases deviate from ideal behavior at high pressure. Which of the following statement(s) is correct for non-ideality?
at high pressure the collision between the gas molecule become enormous
at high pressure the gas molecules move only in one direction
at high pressure, the volume of gas become insignificant
at high pressure the intermolecular interactions become significant
Rate of diffusion of a gas is
directly proportional to its density
directly proportional to its molecular weight
directly proportional to its square root of its molecular weight
inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular weight
Which of the following is the correct expression for the equation of state of van der Waals gas?
`["P" + "a"/("n"^2"V"^2)]("V" - "nb") = "nRT"`
`["P" + "na"/("n"^2"V"^2)]("V" - "nb") = "nRT"`
`["P" + "an"^2/("V"^2)]("V" - "nb") = "nRT"`
`["P" + ("n"^2"a"^2)/("V"^2)]("V" - "nb") = "nRT"`
When an ideal gas undergoes unrestrained expansion, no cooling occurs because the molecules
are above inversion temperature
exert no attractive forces on each other
do work equal to the loss in kinetic energy
collide without loss of energy
Equal weights of methane and oxygen are mixed in an empty container at 298 K. The fraction of total pressure exerted by oxygen is
`1/3`
`1/2`
`2/3`
`1/3 xx 273 xx 298`
The temperatures at which real gases obey the ideal gas laws over a wide range of pressure is called __________.
Critical temperature
Boyle temperature
Inversion temperature
Reduced temperature
In a closed room of 1000 m3 a perfume bottle is opened up. The room develops a smell. This is due to which property of gases?
Viscosity
Density
Diffusion
None
A bottle of ammonia and a bottle of HCl connected through a long tube are opened simultaneously at both ends. The white ammonium chloride ring first formed will be
At the center of the tube
Near the hydrogen chloride bottle
Near the ammonia bottle
Throughout the length of the tube
The value of the universal gas constant depends upon
Temperature of the gas
Volume of the gas
Number of moles of the gas
Units of pressure and volume
The value of the gas constant R is
0.082 dm3 atm
0.987 cal mol-1 K-1
8.3 J mol-1 K-1
8 erg mol-1 K-1
Use of hot air balloon in sports and meteorological observation is an application of
Boyle’s law
Newton’s law
Kelvin’s law
Brown’s law
The table indicates the value of van der Waals constant ‘a’ in (dm3)2 atm. mol-2
| Gas | O2 | N2 | NH3 | CH4 |
| a | 1.360 | 1.390 | 4.170 | 2.253 |
The gas which can be most easily liquefied is
O2
N2
NH3
CH4
Consider the following statements
i) Atmospheric pressure is less at the top of a mountain than at sea level
ii) Gases are much more compressible than solids or liquids
iii) When the atmospheric pressure increases the height of the mercury column rises
Select the correct statement
i and ii
ii and iii
i and iii
i, ii and iii
Compressibility factor for CO2 at 400 K and 71.0 bar is 0.8697. The molar volume of CO2 under these conditions is
22.04 dm3
2.24 dm3
0.41 dm3
19.5 dm3
If the temperature and volume of an ideal gas is increased to twice its values, the initial pressure P becomes
4P
2P
P
3P
At identical temperature and pressure, the rate of diffusion of hydrogen gas is `3sqrt3` times that of a hydrocarbon having molecular formula CnH2n–2. What is the value of n?
8
4
3
1
Equal moles of hydrogen and oxygen gases are placed in a container, with a pin-hole through which both can escape what fraction of oxygen escapes in the time required for one-half of the hydrogen to escape.
`3/8`
`1/2`
`1/8`
`1/4`
The variation of volume V, with temperature T, keeping the pressure constant is called the coefficient of thermal expansion ie α = `1/"V"((∂"V")/(∂"T"))_"P"`. For an ideal gas α is equal to
T
`1/"T"`
P
none of these
Four gases P, Q, R and S have almost the same values of 'b' but their 'a' values (a, b are Van der Waals Constants) are in the order Q < R < S < P. At a particular temperature, among the four gases, the most easily liquefiable one is
P
Q
R
S
Maximum deviation from ideal gas is expected from
\[\ce{CH4_{(g)}}\]
\[\ce{NH3_{(g)}}\]
\[\ce{H2_{(g)}}\]
\[\ce{N2_{(g)}}\]
The units of Van der Waals constants 'b' and 'a' respectively
mol L-1 and L atm2 mol-1
mol L and L atm mol2
mol-1 L and L2 atm mol-2
none of these
Assertion: Critical temperature of CO2 is 304 K, it can be liquefied above 304 K.
Reason: For a given mass of gas, volume is to directly proportional to pressure at constant temperature
both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
assertion is true but reason is false
both assertion and reason are false
What is the density of N2 gas at 227°C and 5.00 atm pressure? (R = 0.082 L atm K–1 mol–1)
1.40 g/L
2.81 g/L
3.41 g/L
0.29 g/L
Which of the following diagrams correctly describes the behaviour of a fixed mass of an ideal gas? (T is measured in K)
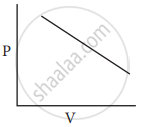
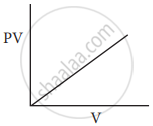
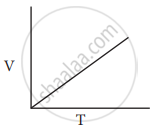
All of these
25 g of each of the following gases are taken at 27°C and 600 mm Hg pressure. Which of these will have the least volume?
HBr
HCl
HF
HI
Write brief answer to the following questions
State Boyle's law.
Name two items that can serve as a model for Gay Lusaac’s law and explain.
Give the mathematical expression that relates gas volume and moles.
What are ideal gases?
In what way real gases differ from ideal gases.
Can a Van der Waals gas with a = 0 be liquefied? explain.
Suppose there is a tiny sticky area on the wall of a container of gas. Molecules hitting this area stick there permanently. Is the pressure greater or less than on the ordinary area of walls?
Explain the following observation.
Aerated water bottles are kept under water during summer
Explain the following observation.
Liquid ammonia bottle is cooled before opening the seal
Explain the following observation.
The type of an automobile is inflated to slightly lesser pressure in summer than in winter
Explain the following observation.
The size of a weather balloon becomes larger and larger as it ascends up to larger altitude
Give a suitable explanation for the following facts about gases.
Gases don’t settle at the bottom of a container
Give a suitable explanation for the following facts about gases.
Gases diffuse through all the space available to them
Suggest why there is no hydrogen (H2) in our atmosphere. Why does the moon have no atmosphere?
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if it is compressed to a smaller volume at a constant temperature.
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if the temperature is raised while keeping the volume constant.
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if more gas is introduced into the same volume and at the same temperature.
Which of the following gases would you expect to deviate from ideal behavior under conditions of low-temperature F2, Cl2, or Br2? Explain.
Distinguish between diffusion and effusion.
Aerosol cans carry a clear warning of the heating of the can. Why?
Would it be easier to drink water with a straw on the top of Mount Everest?
Write the Van der Waals equation for a real gas. Explain the correction term for pressure and volume.
Derive the values of critical constants in terms of van der Waals constants.
Why do astronauts have to wear protective suits when they are on the surface of the moon?
When ammonia combines with HCl, NH4Cl is formed as white dense fumes. Why do more fumes appear near HCl?
A sample of gas at 15°C at 1 atm. has a volume of 2.58 dm3. When the temperature is raised to 38°C at 1 atm does the volume of the gas Increase? If so, calculate the final volume.
A sample of gas has a volume of 8.5 dm3 at an unknown temperature. When the sample is submerged in ice water at 0°C, its volume gets reduced to 6.37 dm3. What is its initial temperature?
Of two samples of nitrogen gas, sample A contains 1.5 moles of nitrogen in a vessel of the volume of 37.6 dm3 at 298 K, and sample B is in a vessel of volume 16.5 dm3 at 298 K. Calculate the number of moles in sample B.
Sulphur hexafluoride is a colourless, odourless gas; calculate the pressure exerted by 1.82 moles of the gas in a steel vessel of volume 5.43 dm3 at 69.5 °C, assuming ideal gas behaviour
Argon is an inert gas used in light bulbs to retard the vaporization of the tungsten filament. A certain light bulb containing argon at 1.2 atm and 18°C is heated to 85°C at constant volume. Calculate its final pressure in atm.
A small bubble rises from the bottom of a lake where the temperature and pressure are 6°C and 4 atm. to the water surface, where the temperature is 25°C and pressure is 1 atm. Calculate the final volume in (mL) of the bubble, if its initial volume is 1.5 mL.
Hydrochloric acid is treated with a metal to produce hydrogen gas. Suppose a student carries out this reaction and collects a volume of 154.4 × 10−3 dm3 of a gas at a pressure of 742 mm of Hg at a temperature of 298 K. What mass of hydrogen gas (in mg) did the student collect?
It takes 192 sec for an unknown gas to diffuse through a porous wall and 84 sec for N2 gas to effuse at the same temperature and pressure. What is the molar mass of the unknown gas?
A tank contains a mixture of 52.5 g of oxygen and 65.1 g of CO2 at 300 K the total pressure in the tanks is 9.21 atm. Calculate the partial pressure (in atm.) of each gas in the mixture.
A combustible gas is stored in a metal tank at a pressure of 2.98 atm at 25°C. The tank can withstand a maximum pressure of 12 atm after which it will explode. The building in which the tank has been stored catches fire. Now predict whether the tank will blow up first or start melting? (Melting point of the metal = 1100 K).
Solutions for 6: Gaseous State
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 6 - Gaseous State Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 6 - Gaseous State - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-volume-1-and-2-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 6 - Gaseous State
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 6 (Gaseous State) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 6 Gaseous State are The Gaseous State, The Gas Laws, Ideal Gas Equation, Mixture of Gases - Dalton’S Law of Partial Pressures, Behaviour of Real Gases: Deviation from Ideal Gas Behaviour, Derivation of Critical Constants from Van Der Waals Constant, Liquefaction of Gases and Critical Constant.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board solutions Gaseous State exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Gaseous State Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry - Volume 1 and 2 [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
