Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If 1 gram of each of the following gases are taken at STP, which of the gases will occupy (a) greatest volume and (b) smallest volume?
\[\ce{CO, H2O, CH4 , NO}\]
Solution
Molar volume of a gas is volume occupied by 1 mole of gas at STP (273.15 K and 1 bar pressure) and is equal to 22700 mL.
28 g of \[\ce{CO}\] occupy volume = 227000 mL
∴ 1 g of CO occupies volume = `22700/28` mL at STP
Similarly, 1 g of \[\ce{H2O}\] occupies volume = `22700/18` mL at STP
1 g of \[\ce{CH4}\] occupies volume = `22700/16` mL at STP
1 g of \[\ce{NO}\] occupies volume = `22700/30` mL at STP
(a) \[\ce{CH4}\] occupies greatest volume.
(b) \[\ce{NO}\] occupies smallest volume.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which of the following is the correct expression for the equation of state of van der Waals gas?
The value of the universal gas constant depends upon
Which of the following diagrams correctly describes the behaviour of a fixed mass of an ideal gas? (T is measured in K)
25 g of each of the following gases are taken at 27°C and 600 mm Hg pressure. Which of these will have the least volume?
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if it is compressed to a smaller volume at a constant temperature.
A plot of volume (V) versus temperature (T) for a gas at constant pressure is a straight line passing through the origin. The plots at different values of pressure are shown in Figure. Which of the following order of pressure is correct for this gas?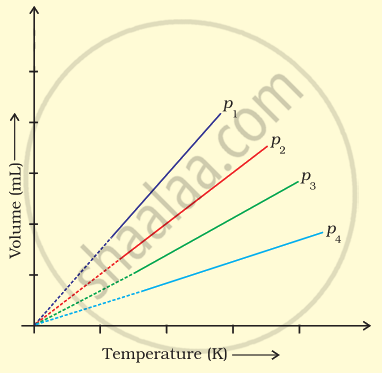
Compressibility factor, Z, of a gas is given as Z = `(pV)/(nRT)`. What is the value of Z for an ideal gas?
Compressibility factor, Z, of a gas is given as Z = `(pV)/(nRT)`. For real gas what will be the effect on value of Z above Boyle’s temperature?
In van der Waal's equation for the real gas, the expression for the net force of attraction amongst the gas molecules is given by:
Choose the correct option for the total pressure (in atm.) in a mixture of 4g \[\ce{O2}\] and 2g \[\ce{H2}\] confined in a total volume of one litre at 0°C is ______.
[Given R = 0.082 L atm mol−1K−1, T = 273 K]
