Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A polariod (I) is placed in front of a monochromatic source. Another polatiod (II) is placed in front of this polaroid (I) and rotated till no light passes. A third polaroid (III) is now placed in between (I) and (II). In this case, will light emerge from (II). Explain.
Solution
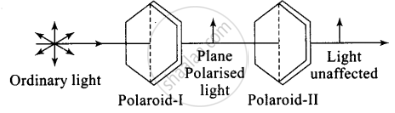
A polaroid (I) is placed in front of a monochromatic source. Another polaroid (II) is placed in front of this polaroid (I) when the pass axis of (II) is parallel to (I), light passes through polaroid-II unaffected.
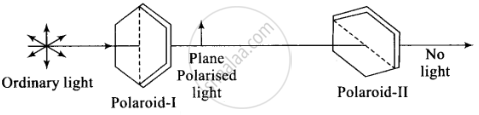
Now polaroid (II) is rotated till no light passes. In this situation, the pass of polaroid (II) is perpendicular to polaroid (I) and then (I) and (II) are set in crossed positions. No light passes through polaroid-II.
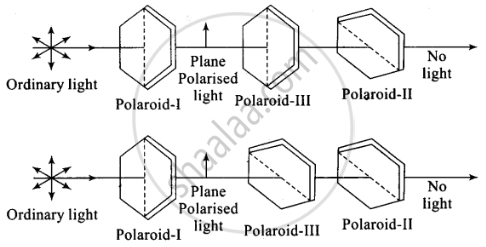
Now third polaroid (III) is now placed in between (I) and (II). Only in the special cases when the pass axis of (III) is parallel to (I) or (II), there shall be no light emerging. In all other cases, there shall be light emerging because the pass axis of (II) is no longer perpendicular to the pass axis of (III).
Now polaroid (II) is rotated till no light passes. In this situation, the pass axis of polaroid (II) is perpendicular to polaroid (I) and then (I) and (II) are set in crossed positions. No light passes through polaroid-II.
Now third polaroid (III) is now placed in between (I) and (II). Only in the special cases when the pass axis of (III) is parallel to (I) or (II), there shall be no light emerging. In all other cases, there shall be light emerging because the pass axis of (II) is no longer perpendicular to the pass axis of (III).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the diffraction pattern due to a single slit of width 'd' with incident light of wavelength 'λ', at an angle of diffraction θ. the condition for first minimum is ....
(a)`lambda sin theta =d`
(b) `d costheta =lambda`
(c)`d sintheta=lambda`
(d) `lambda cos theta=d`
Describe briefly how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a single narrow slit illuminated by a monochromatic source of light. Hence obtain the conditions for the angular width of secondary maxima and secondary minima.
In Fraunhofer diffraction, how is the angular width of the central bright fringe affected when slit separation is increased?
Draw the intensity distribution for the diffraction bands produced due to single slit ?
Monochromatic light of wavelength 4300 Å falls on a slit of width ‘a’. For what value of ‘a’ the first maximum falls at 30° ?
Wavelength of light of frequency 100 Hz is
Consider the diffraction pattern for a small pinhole. As the size of the hole is increased ______.
- the size decreases.
- the intensity increases.
- the size increases.
- the intensity decreases.
Write two points of difference between an interference pattern and a diffraction pattern.
In a diffraction pattern due to a single slit, how will the angular width of the central maximum change, if the screen is moved closer to the slit?
Justify your answer.
In the diagram shown, the separation between the slit is equal to 3λ, where λ is the wavelength of the light incident on the plane of the slits. A thin film of thickness 3λ and refractive index 2 has been placed in the front of the upper slit. The distance of the central maxima on the screen from O is ______.