Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A right-angled triangle may have all sides equal.
Options
True
False
Solution
This statement is False.
Explanation:
Hypotenuse is always greater than the other two sides of the right-angled triangle.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Prove that the diagonals of a rectangle ABCD, with vertices A(2, -1), B(5, -1), C(5, 6) and D(2, 6), are equal and bisect each other.
A man goes 10 m due east and then 24 m due north. Find the distance from the starting point
In figure, ∠B of ∆ABC is an acute angle and AD ⊥ BC, prove that AC2 = AB2 + BC2 – 2BC × BD
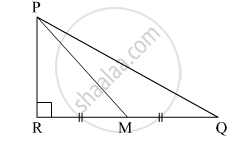
In the given figure, M is the midpoint of QR. ∠PRQ = 90°. Prove that, PQ2 = 4PM2 – 3PR2.
In an isosceles triangle ABC; AB = AC and D is the point on BC produced.
Prove that: AD2 = AC2 + BD.CD.
From the given figure, find the length of hypotenuse AC and the perimeter of ∆ABC.
In a triangle ABC, AC > AB, D is the midpoint BC, and AE ⊥ BC. Prove that: AB2 = AD2 - BC x CE + `(1)/(4)"BC"^2`
A point OI in the interior of a rectangle ABCD is joined with each of the vertices A, B, C and D. Prove that OB2 + OD2 = OC2 + OA2
If ‘l‘ and ‘m’ are the legs and ‘n’ is the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle then, l2 = ________
A flag pole 18 m high casts a shadow 9.6 m long. Find the distance of the top of the pole from the far end of the shadow.
