Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A rope of negligible mass is wound round a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N? What is the linear acceleration of the rope? Assume that there is no slipping.
Solution
Mass of the hollow cylinder, m = 3 kg
Radius of the hollow cylinder, r = 40 cm = 0.4 m
Applied force, F = 30 N
The moment of inertia of the hollow cylinder about its geometric axis:
I = mr2
= 3 × (0.4)2 = 0.48 kg m2
Torque, t = F x r
= 30 × 0.4 = 12 Nm
For angular acceleration `alpha`, torque is also given by the relation:
`t = Ialpha`
`alpha = t/I = 12/0.48`
`= 25 " rad s"^(-2)`
Linear acceleration = `ralpha = 0.4 xx 25 = 10 ms^(-2)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Given the moment of inertia of a disc of mass M and radius R about any of its diameters to be MR2/4, find its moment of inertia about an axis normal to the disc and passing through a point on its edge
A child stands at the centre of a turntable with his two arms outstretched. The turntable is set rotating with an angular speed of 40 rev/min. How much is the angular speed of the child if he folds his hands back and thereby reduces his moment of inertia to 2/5 times the initial value? Assume that the turntable rotates without friction.
A cylinder of mass 10 kg and radius 15 cm is rolling perfectly on a plane of inclination 30°. The coefficient of static friction µs = 0.25.
(a) How much is the force of friction acting on the cylinder?
(b) What is the work done against friction during rolling?
(c) If the inclination θ of the plane is increased, at what value of θ does the cylinder begin to skid, and not roll perfectly?
The moment of inertia of a uniform semicircular wire of mass M and radius r about a line perpendicular to the plane of the wire through the centre is ___________ .
A body having its centre of mass at the origin has three of its particles at (a,0,0), (0,a,0), (0,0,a). The moments of inertia of the body about the X and Y axes are 0⋅20 kg-m2 each. The moment of inertia about the Z-axis
Solve the previous problem if the friction coefficient between the 2⋅0 kg block and the plane below it is 0⋅5 and the plane below the 4⋅0 kg block is frictionless.
A uniform metre stick of mass 200 g is suspended from the ceiling thorough two vertical strings of equal lengths fixed at the ends. A small object of mass 20 g is placed on the stick at a distance of 70 cm from the left end. Find the tensions in the two strings.
Two blocks of masses 400 g and 200 g are connected through a light string going over a pulley which is free to rotate about its axis. The pulley has a moment of inertia \[1 \cdot 6 \times {10}^{- 4} kg - m^2\] and a radius 2⋅0 cm, Find (a) the kinetic energy of the system as the 400 g block falls through 50 cm, (b) the speed of the blocks at this instant.
From a circular ring of mass ‘M’ and radius ‘R’ an arc corresponding to a 90° sector is removed. The moment of inertia of the remaining part of the ring about an axis passing through the centre of the ring and perpendicular to the plane of the ring is ‘K’ times ‘MR2’. Then the value of ‘K’ is ______.
Consider a badminton racket with length scales as shown in the figure.
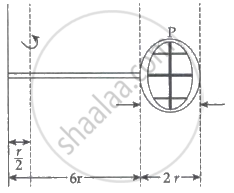
If the mass of the linear and circular portions of the badminton racket is the same (M) and the mass of the threads is negligible, the moment of inertia of the racket about an axis perpendicular to the handle and in the plane of the ring at, `r/2` distance from the ends A of the handle will be ______ Mr2.
