Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
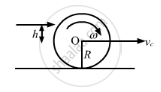
A thin spherical shell of radius R lying on a rough horizontal surface is hit sharply and horizontally by a cue. Where should it be hit so that the shell does not slip on the surface?
Solution
If the shell does not slip on the surface, its motion should be pure rolling.
Let the cue hits at a height 'h' above the centre.
Let the centre of shell moves with velocity vc and shell rotates with angular velocity ω after hitting.
For pure rolling,
\[v_c = R\omega\]
On applying the law of conservation of angular momentum at point O, we get
\[m v_c h = I\omega\]
\[m v_c h = \frac{2}{3}m R^2 \left( \frac{v_c}{R} \right)\]
\[h = \frac{2R}{3}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two bodies make an elastic head-on collision on a smooth horizontal table kept in a car. Do you expect a change in the result if the car is accelerated in a horizontal road because of the non inertial character of the frame? Does the equation "Velocity of separation = Velocity of approach" remain valid in an accelerating car? Does the equation "final momentum = initial momentum" remain valid in the accelerating car?
Use the definition of linear momentum from the previous question. Can we state the principle of conservation of linear momentum for a single particle?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Take "the table plus the ball" as the system. friction between the table and the ball is then an internal force. As the ball slows down, the momentum of the system decreases. Which external force is responsible for this change in the momentum?
When a nucleus at rest emits a beta particle, it is found that the velocities of the recoiling nucleus and the beta particle are not along the same straight line. How can this be possible in view of the principle of conservation of momentum?
Consider the following two statements:
(A) Linear momentum of a system of particles is zero.
(B) Kinetic energy of a system of particles is zero.
A bullet hits a block kept at rest on a smooth horizontal surface and gets embedded into it. Which of the following does not change?
A nucleus moving with a velocity \[\vec{v}\] emits an α-particle. Let the velocities of the α-particle and the remaining nucleus be v1 and v2 and their masses be m1 and m2.
A shell is fired from a cannon with a velocity V at an angle θ with the horizontal direction. At the highest point in its path, it explodes into two pieces of equal masses. One of the pieces retraces its path to the cannon. The speed of the other piece immediately after the explosion is
A block moving in air breaks in two parts and the parts separate
(a) the total momentum must be conserved
(b) the total kinetic energy must be conserved
(c) the total momentum must change
(d) the total kinetic energy must change
A uranium-238 nucleus, initially at rest, emits an alpha particle with a speed of 1.4 × 107m/s. Calculate the recoil speed of the residual nucleus thorium-234. Assume that the mass of a nucleus is proportional to the mass number.
A neutron initially at rest, decays into a proton, an electron, and an antineutrino. The ejected electron has a momentum of 1.4 × 10−26 kg-m/s and the antineutrino 6.4 × 10−27kg-m/s.
Find the recoil speed of the proton
(a) if the electron and the antineutrino are ejected along the same direction and
(b) if they are ejected along perpendicular directions. Mass of the proton = 1.67 × 10−27 kg.
A 60 kg man skating with a speed of 10 m/s collides with a 40 kg skater at rest and they cling to each other. Find the loss of kinetic energy during the collision.
A bullet of mass 20 g travelling horizontally with a speed of 500 m/s passes through a wooden block of mass 10.0 kg initially at rest on a level surface. The bullet emerges with a speed of 100 m/s and the block slides 20 cm on the surface before coming to rest. Find the friction coefficient between the block and the surface (See figure).
The blocks shown in figure have equal masses. The surface of A is smooth but that of Bhas a friction coefficient of 0.10 with the floor. Block A is moving at a speed of 10 m/s towards B which is kept at rest. Find the distance travelled by B if (a) the collision is perfectly elastic and (b) the collision is perfectly inelastic.
Suppose the particle of the previous problem has a mass m and a speed \[\nu\] before the collision and it sticks to the rod after the collision. The rod has a mass M. (a) Find the velocity of the centre of mass C of the system constituting "the rod plus the particle". (b) Find the velocity of the particle with respect to C before the collision. (c) Find the velocity of the rod with respect to C before the collision. (d) Find the angular momentum of the particle and of the rod about the centre of mass C before the collision. (e) Find the moment of inertia of the system about the vertical axis through the centre of mass C after the collision. (f) Find the velocity of the centre of mass C and the angular velocity of the system about the centre of mass after the collision.
A sphere starts rolling down an incline of inclination θ. Find the speed of its centre when it has covered a distance l.
The following figure shows a rough track, a portion of which is in the form of a cylinder of radius R. With what minimum linear speed should a sphere of radius r be set rolling on the horizontal part so that it completely goes round the circle on the cylindrical part.

The track shown is figure is frictionless. The block B of mass 2m is lying at rest and the block A or mass m is pushed along the track with some speed. The collision between Aand B is perfectly elastic. With what velocity should the block A be started to get the sleeping man awakened?

