Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer in brief.
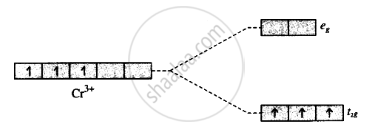
With the help of the crystal field, the energy-level diagram explains why the complex [Cr(en)3]3⊕ is coloured.
Solution
CFT:
ligands are treated as point charges interaction, but ligands & metal are purely electrostatic.
Metal has dorbital = dxy, dxz, dyz, dx2, dy2, dz2
When ligands approach metal, the degeneracy of metal is disturbed.
spit int 2 energy levels = t2g & eg
dxy, dxz, dxz
[Cr(en)3]+3 = en = ethylene diamine bidentate ligand
n = 3
`sqrt(n(n+2)) = sqrt(3(3+2))`
`sqrt15`
= 3.83 B.M
Paramagnetic :
d - d transition = [Cr(en)3]+3 = coloured property
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer in brief.
[CoCl4]2- is a tetrahedral complex. Draw its box orbital diagram. State which orbitals participate in hybridization.
Answer in brief.
[CoCl4]2- is a tetrahedral complex. Draw its box orbital diagram. State which orbitals participate in hybridization.
Answer in brief.
What are strong field and weak field ligands ? Give one example of each.
Identify the number of donor groups present in EDTA.
Chlorophyll and haemoglobin are complexes of ____________ respectively.
The number of unpaired electrons in the complex ion [CoF6]3− is ____________.
The INCORRECT match for complex with its geometry is:
The number of unpaired electrons in the complex ion [NiCl4]2− is ____________.
Identify the CORRECT statements regarding [Co(NH3)6]3+.
I. Oxidation state of metal ion = +3
II. It is a high spin complex.
III. It is paramagnetic.
IV. Metal ion undergoes d2sp3 hybridization.
Which one of the following complexes can exhibit geometrical isomerism?
What is the value of primary valence of Co in CoCl3?
What is the type of magnetic behavior and geometry respectively in Cuproammonium sulphate (Atomic number of Cu = 29)?
Identify the increasing order of effective magnetic moment of the following elements in their +2 oxidation state.
[Fe (Z = 26), Co (Z = 27), Ni (Z = 28), Cu (Z = 29)]
Which of the following types of square planar complexes can show geometrical isomerism [M = metal, a, b, = monodentate ligand]?
A compound forms hcp structure. What is the number of (a) octahedral voids, (b) tetrahedral voids, (c) total voids formed in 0.2 mol of the compound?
Give a valence bond description of the bonding in the high spin complex [MnCl6]3− Include orbital diagram for the free metal ion and the metal ion in the complex. Indicate which hybrid orbitals the metal ion uses for bonding. Specify the number of unpaired electrons.
A compound forms a hep structure. Calculate the number of octahedral voids in 0.4 mol. (NA = 6.022 × 1023).
Octahedral complex have ______ hybridisation.
Give the limitations of VBT.
A compound forms hexagonal close packed (hcp) structure. What is the number of (i) Octahedral voids, (ii) Tetrahedral voids, (iii) Total voids formed in 0.7 mol of it.
Mention the number of unpaired electrons and geometry of the following complex:
\[\ce{[Ni(Cl)4]^{2-}}\]
Mention the number of unpaired electrons and geometry of the following complex:
\[\ce{[Ni(CN)4]^2-}\]
