Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
BCl3 exists as monomer whereas AlCl3 is dimerised through halogen bridging. Give reason. Explain the structure of the dimer of AlCl3 also.
Solution
Both the compounds, BCl3 and AlCl3 are electron-deficient compounds. In BCl3, boron is smaller in size and cannot assemble four big chlorine atoms near it causing steric hindrance and making it unstable.
Hence, BCl3 exists as a monomer only.
In AlCl3, aluminum has 3p-orbitals through which chlorine atoms can be accommodated easily to complete its octet and dimer is formed.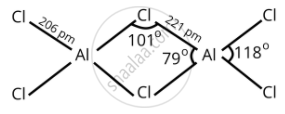
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If B–Cl bond has a dipole moment, explain why BCl3 molecule has zero dipole moment.
In some of the reactions thallium resembles aluminium, whereas in others it resembles with group I metals. Support this statement by giving some evidences.
Ionisation enthalpy (∆iH1kJ mol–1) for the elements of Group 13 follows the order.
The most commonly used reducing agent is ______.
When BCl3 is treated with water, it hydrolyses and forms [B[OH]4]– only whereas AlCl3 in acidified aqueous solution forms [Al(H2O)6]3+ ion. Explain what is the hybridisation of boron and aluminium in these species?
Explain the following:
Pb4+ acts as an oxidising agent but Sn2+ acts as a reducing agent.
Match the species given in Column I with the hybridisation given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Boron in [B(OH)4]– | (a) sp2 |
| (ii) Aluminium in [Al(H2O)6]3+ | (b) sp3 |
| (iii) Boron in B2H6 | (c) sp3d2 |
| (iv) Carbon in Buckminsterfullerene | |
| (v) Silicon in \[\ce{SiO^{4-}4}\] | |
| (vi) Germanium in [GeCl6]2– |
Boron fluoride exists as BF3 but boron hydride doesn’t exist as BH3. Give reason. In which form does it exist? Explain its structure.
A nonmetallic element of group 13, used in making bullet proof vests is extremely hard solid of black colour. It can exist in many allotropic forms and has unusually high melting point. Its trifluoride acts as Lewis acid towards ammonia. The element exihibits maximum covalency of four. Identify the element and write the reaction of its trifluoride with ammonia. Explain why does the trifluoride act as a Lewis acid.
Boron compounds behave as Lewis acids because of their ______.
