Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Can you think of two particles which do not exert gravitational force on each other?
Solution
No. All practicals which have mass exert gravitational force on each other. Even massless particles experience the same gravitational force like other particles, because they do have relativistic mass.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
If the moon attracts the earth, why does the earth not move towards the moon?
Calculate the force of gravitation between the earth and the Sun, given that the mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and of the Sun = 2 × 1030 kg. The average distance between the two is 1.5 × 1011 m.
If you compare the gravitational force on the Earth due to the Sun to that due to the Moon, you would find that the Sun’s pull is greater than the Moon’s pull. (You can check this yourself using the data available in the succeeding exercises). However, the tidal effect of the Moon’s pull is greater than the tidal effect of Sun. Why?
Write the three laws given by Kepler. How did they help Newton to arrive at the inverse square law of gravity?
Suppose the gravitational potential due to a small system is k/r2 at a distance r from it. What will be the gravitational field? Can you think of any such system? What happens if there were negative masses?
Inside a uniform spherical shell
(a) the gravitational potential is zero
(b) the gravitational field is zero
(c) the gravitational potential is same everywhere
(d) the gravitational field is same everywhere
Consider a planet moving in an elliptical orbit round the sun. The work done on the planet by the gravitational force of the sun
(a) is zero in any small part of the orbit
(b) is zero in some parts of the orbit
(c) is zero in one complete revolution
(d) is zero in no part of the motion.
Which of the following quantities remain constant in a planetary motion (consider elliptical orbits) as seen from the sun?
Three equal masses m are placed at the three corners of an equilateral triangle of side a. Find the force exerted by this system on another particle of mass m placed at (a) the mid-point of a side, (b) at the centre of the triangle.
A tunnel is dug along a diameter of the earth. Find the force on a particle of mass m placed in the tunnel at a distance x from the centre.
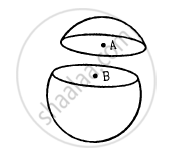
A thin spherical shell having uniform density is cut in two parts by a plane and kept separated as shown in the following figure. The point A is the centre of the plane section of the first part and B is the centre of the plane section of the second part. Show that the gravitational field at A due to the first part is equal in magnitude to the gravitational field at B due to the second part.
The mass of moon is about 0.012 times that of earth and its diameter is about 0.25 times that of earth. The value of G on the moon will be:
Write an expression for the gravitational force of attraction between two bodies of masses m1 and m2 separated by a distance r.
The acceleration produced by a force in an object is directly proportional to the applied _________ And inversely proportional to the _________ Of the object.
Why don't you feel the force of attraction between your friend sitting close to you and yourself?
A ball is thrown up with a speed of 4.9 ms-1.
Calculate the time it takes to reach this height.
A ball is thrown up with a speed of 4.9 ms-1.
Prove that the time of ascent is equal to the time of descent.
Two equal and opposite forces acting at the same point on a stationary body. Will the body move? Give reason to explain your answer.
Answer the following question.
State Newton’s law of gravitation and express it in vector form.
