Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Three equal masses m are placed at the three corners of an equilateral triangle of side a. Find the force exerted by this system on another particle of mass m placed at (a) the mid-point of a side, (b) at the centre of the triangle.
Solution
(a) Consider that mass 'm' is placed at the midpoint O of side AB of equilateral triangle ABC.
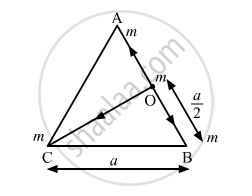
AO = BO = \[\frac{a}{2}\]
Then \[\overrightarrow{F}_{OA} = \frac{4G m^2}{a^2}\] along OA
Also, \[\overrightarrow{F}_{OB} = \frac{4 G m^2}{a^2}\]along OB
OC = \[\frac{\sqrt{3}a}{2}\]
\[\overrightarrow{F}_{OC} = \frac{4 G m^2}{\left\{ \left( 3 \right) a^2 \right\}} = \frac{4G m^2}{3 a^2}\] along OC
The net force on the particle at O is \[\overrightarrow{F} = \overrightarrow{F}_{OA} + \overrightarrow{F}_{OB} + \overrightarrow{F}_{OC}\]
Since equal and opposite forces cancel each other, we have :
\[\overrightarrow{F} = \overrightarrow{F}_{OC} = \frac{4 G m^2}{\left\{ \left( 3 \right) a^2 \right\}} = \frac{4G m^2}{3 a^2}\] along OC.
(b) If the particle placed at O (centroid)
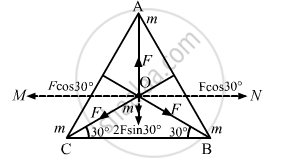
All the forces are equal in magnitude but their directions are different as shown in the figure.
Equal and opposite forces along OM and ON cancel each other.
i.e., \[F\cos30^\circ= F\cos30^\circ\]
∴ Resultant force \[= F - 2F\sin30 = 0\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
What happens to the force between two objects, if the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
What happens to the force between two objects, if the masses of both objects are doubled?
Choose the correct alternative:
Acceleration due to gravity increases/decreases with increasing altitude.
State Kepler’s law which is represented by the relation r3 ∝ T2.
At noon, the sun and the earth pull the objects on the earth's surface in opposite directions. At midnight, the sun and the earth pull these objects in same direction. Is the weight of an object, as measured by a spring balance on the earth's surface, more at midnight as compared to its weight at noon?
Suppose the gravitational potential due to a small system is k/r2 at a distance r from it. What will be the gravitational field? Can you think of any such system? What happens if there were negative masses?
The weight of an object is more at the poles than at the equator. Is it beneficial to purchase goods at equator and sell them at the pole? Does it matter whether a spring balance is used or an equal-beam balance is used?
A body is suspended from a spring balance kept in a satellite. The reading of the balance is W1 when the satellite goes in an orbit of radius R and is W2 when it goes in an orbit of radius 2 −R.
Write an expression for the gravitational force of attraction between two bodies of masses m1 and m2 separated by a distance r.
The acceleration produced by a force in an object is directly proportional to the applied _________ And inversely proportional to the _________ Of the object.
A ball is thrown up with a speed of 4.9 ms-1.
Calculate the time it takes to reach this height.
A ball is thrown up with a speed of 4.9 ms-1.
Prove that the time of ascent is equal to the time of descent.
Where will you weigh more: at the moon's surface or at the earth's surface?
You can change the direction in which an object is moving by___________.
Why does a ball moving on a table top eventually stops?
Law of gravitation gives the gravitational force between
Three uniform spheres, each having mass m and radius r, are kept in such a way that each touches the other two. The magnitude of the gravitational force on any sphere due to the other two is
Different points in earth are at slightly different distances from the sun and hence experience different forces due to gravitation. For a rigid body, we know that if various forces act at various points in it, the resultant motion is as if a net force acts on the c.m. (centre of mass) causing translation and a net torque at the c.m. causing rotation around an axis through the c.m. For the earth-sun system (approximating the earth as a uniform density sphere).
Two particles of equal mass 'm' go around a circle of radius R under the action of their mutual gravitational attraction. The speed of each particle with respect to its centre of mass is ______.
