Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following sentence.
A ray of light strikes the glass slab at an angle of 50°. What is the angle of incidence?
Options
50°
90°
60°
40°
Solution
40°
The ray of light strikes at an angle of 50 with the horizontal. The angle of incidence is with respect to the normal, so the angle of incidence is 90° − 50° = 40°.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain how spectrum is formed.
Study the following four experimental set-ups I, II, III and IV for the experiment, "To trace the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass slab."
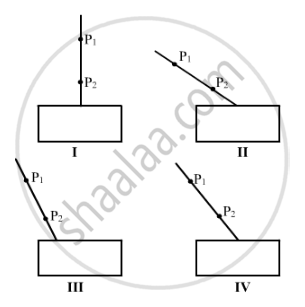
Which of the marked set-ups is likely to give best results (P1 and P2 are the positions of pins fixed on the incident ray)?
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
Write a relationship between the angle of incidence and angle of refractions for a given pair of media
Name a prism required for obtaining a spectrum of Ultraviolet light.
How is the refractive index of a medium related to the speed of light in it?
A light ray in passing from water to a medium
(a) speeds up
(b) slows down. In each case, give one example of the medium.
Name the colour of white light which is deviated the most on passing through a prism.
A ray of light enters a glass slab ABDC as shown in figure and strikes at the centre O of the circular part AC of the slab. The critical angle of glass is 42°. Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out from the slab. Mark the angles in the diagram wherever necessary.

Select from the following the best experimental set-up for tracing the path of a ray of light through a glass slab: (A) I
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
A ray of light falls normally on the surface of a transparent glass slab. Draw a ray diagram to show its path and also mark angle of incidence and angle of emergence.
Rahim recorded the following sets of observations while tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence.
|
S. No. |
Angle of incidence |
Angle of refraction |
Angle of emergence |
|
I |
45° |
41° |
45° |
|
II |
40° |
38° |
38° |
|
III |
45° |
41° |
40° |
|
IV |
41° |
45° |
41° |
The correct observation is recorded at serial number:
(1) I
(2) II
(3) III
(4) IV
Four students A, B, C and D traced the paths of incident ray and the emergent ray by fixing pins P and Q for incident ray and pins R and S for emergent ray for a ray of light passing through a glass slab.
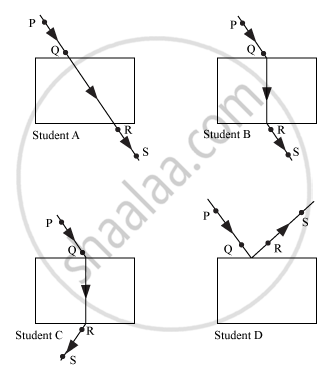
The correct emergent ray was traced by the student:
(1) A
(2) B
(3) C
(4) D
-
- the angle of refraction and
- the angle of deviation for the ray?
Fill in the blank to complete the following sentence:
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, it bends ...........
In the fig., PO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass block.
(a) Complete the path of the ray through the block.
(b) In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles I and r?
(c) Mark angle of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
(d) Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
(e) Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray.
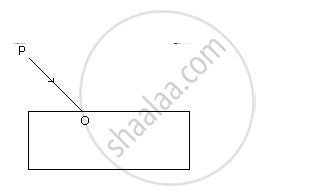
Fig shows a lens as a combination of a glass block and two prisms.
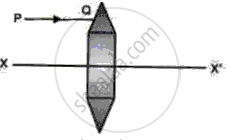
(i) Name the lens formed by the combination.
(ii) what is the XX' called?
(iii) Complete the ray diagram and show the path of the incident ray PQ after passing through the lens.
(iv) The final emergent ray will either meet XX' at a point or appear to come from a point on XX'. what is the point called?
Light of a single colour is passed through a liquid having a piece of glass suspended in it. On changing the temperature of liquid, at a particular temperature, the glass piece is not seen.
Why is the light of a single colour used ?
How does the deviation produced by a prism depend on the refraction index of its material.
The critical angle for glass-air interface is :
Why do the faces of persons sitting around campfire appear to shimmer?
Why upper surface of water contained in a beaker and above eye level appears silvery?
Glass is transparent in nature. Why does glass powder look opaque? When water is poured over it, it again becomes transparent. Why?
State the relation between the refractive index μ and the velocity of light (vm) in that medium.
Comment on the statement ‘The refractive index of glass is 3/2.’
Define the term refractive index of a medium in terms of velocity of light.
Name two instruments of the total refracting prism in which is used.
In what condition a prism is said to be in the position of minimum deviation? What is the direction of the refracted ray inside the prism in this condition?
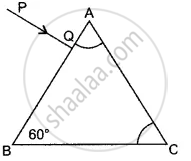
In the diagram alongside a ray of light, PQ is incident normally on one face AB of an equilateral glass prism. What is the angle of incidence at the faces AB and AC?
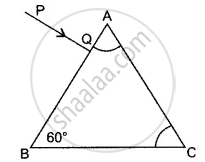
Complete the ray diagram showing its emergence into the air after passing through the prism.
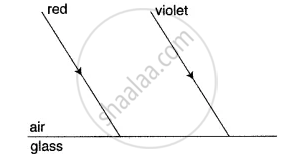
Two parallel rays of Red and Violet travelling through the air, meet the air-glass boundary as shown in the above figure. Will their paths inside the glass be parallel? Give a reason for your answer.
A ray of monochromatic light is incident from the air on a glass slab:
(i) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing the change in the path of the ray till it emerges from the glass slab.
(ii) Name the two rays that are parallel to each other.
(iii) Mark the lateral displacement in your diagram.
The diagram shows the path of a ray of light through a rectangular glass block placed in a liquid of uniform density.

Show with the help of a ray diagram the path of the ray when incident ray normally falls on the first surface of the glass block and passes through the block and the liquid.
Draw a diagram of a prism and label:
(i) the base,
(ii) the refracting surfaces,
(iii) the refracting edge,
(iv) the refracting angle in it.
Calculate the velocity of light in a glass block of refractive index 1.5. (Velocity of light in air = 3 × 108 m/s)
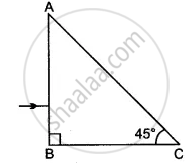
Write the approximate values of speed of light in (i) air and (ii) glass. Use these values to calculate the refractive index of glass with respect to air.
