Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
(a) Derive the relation between the decay constant and half life of a radioactive substance.
(b) A radioactive element reduces to 25% of its initial mass in 1000 years. Find its half life.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an α-particle. Consider the following decay processes:
\[\ce{^223_88Ra -> ^209_82Pb + ^14_6C}\]
\[\ce{^223_88 Ra -> ^219_86 Rn + ^4_2He}\]
Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed.
A radioactive nucleus 'A' undergoes a series of decays as given below:
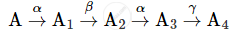
The mass number and atomic number of A2 are 176 and 71 respectively. Determine the mass and atomic numbers of A4 and A.
Define 'activity' of a radioactive substance ?
Two different radioactive elements with half lives T1 and T2 have N1 and N2 undecayed atoms respectively present at a given instant. Derive an expression for the ratio of their activities at this instant in terms of N1 and N2 ?
In a given sample, two radioisotopes, A and B, are initially present in the ration of 1 : 4. The half lives of A and B are respectively 100 years and 50 years. Find the time after which the amounts of A and B become equal.
The half-life of 40K is 1.30 × 109 y. A sample of 1.00 g of pure KCI gives 160 counts s−1. Calculate the relative abundance of 40K (fraction of 40K present) in natural potassium.
A radioactive element disintegrates for an interval of time equal to its mean lifetime. The fraction that has disintegrated is ______
The half-life of the radioactive substance is 40 days. The substance will disintegrate completely in
When a nucleus in an atom undergoes a radioactive decay, the electronic energy levels of the atom ______.
The half-life of `""_82^210Pb` is 22.3 y. How long will it take for its activity 0 30% of the initial activity?
