Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The half-life of 40K is 1.30 × 109 y. A sample of 1.00 g of pure KCI gives 160 counts s−1. Calculate the relative abundance of 40K (fraction of 40K present) in natural potassium.
Solution
Given:
Half-life period of 40K, `T_"1/2"` = 1.30 × 109 years
Count given by 1 g of pure KCI, A = 160 counts/s
Disintegration constant, `lambda = 0.693/T_"1/2"`
Now, activity, A = λN
⇒ `160 = 0.693/t_"1/2" xx N`
⇒ `160 = (0.693/(1.30 xx 10^9 xx 365 xx 86400)) xx N`
⇒ `N = (160 xx 1.30 xx 365 xx 86400 xx 10^9)/0.693`
⇒ `N = 9.5 xx 10^18`
6.023 × 1023 atoms are present in 40 gm.
Thus , `9.5 xx 1018` atoms will be present in `(40 xx 9.5 xx 10^18)/(6.023 xx 10^23)` gm.
= `(4 xx 9.5 xx 10^-4)/6.023` gm
= `6.309 xx 10^-4`
= 0.00063 gm
Relative abundance of 40K in natural potassium = (2 × 0.00063 × 100)% = 0.12%
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to a) 3.125%, b) 1% of its original value?
The half-life of `""_38^90 "Sr"` is 28 years. What is the disintegration rate of 15 mg of this isotope?
The Q value of a nuclear reaction \[\ce{A + b → C + d}\] is defined by
Q = [ mA+ mb− mC− md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^1_1H + ^3_1H -> ^2_1H + ^2_1H}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12"C")` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an α-particle. Consider the following decay processes:
\[\ce{^223_88Ra -> ^209_82Pb + ^14_6C}\]
\[\ce{^223_88 Ra -> ^219_86 Rn + ^4_2He}\]
Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed.
A radioactive nucleus 'A' undergoes a series of decays as given below:
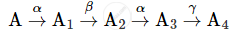
The mass number and atomic number of A2 are 176 and 71 respectively. Determine the mass and atomic numbers of A4 and A.
A radioactive nucleus ‘A’ undergoes a series of decays according to the following scheme:
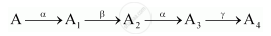
The mass number and atomic number of A are 180 and 72 respectively. What are these numbers for A4?
The decay constant of a radioactive sample is λ. The half-life and the average-life of the sample are respectively
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
57Co decays to 57Fe by β+- emission. The resulting 57Fe is in its excited state and comes to the ground state by emitting γ-rays. The half-life of β+- decay is 270 days and that of the γ-emissions is 10−8 s. A sample of 57Co gives 5.0 × 109 gamma rays per second. How much time will elapse before the emission rate of gamma rays drops to 2.5 × 109per second?
Identify the nature of the radioactive radiations emitted in each step of the decay process given below.
`""_Z^A X -> _Z^A _-1^-4 Y ->_Z^A _-1^-4 W`
The isotope \[\ce{^57Co}\] decays by electron capture to \[\ce{^57Fe}\] with a half-life of 272 d. The \[\ce{^57Fe}\] nucleus is produced in an excited state, and it almost instantaneously emits gamma rays.
(a) Find the mean lifetime and decay constant for 57Co.
(b) If the activity of a radiation source 57Co is 2.0 µCi now, how many 57Co nuclei does the source contain?
c) What will be the activity after one year?
Before the year 1900 the activity per unit mass of atmospheric carbon due to the presence of 14C averaged about 0.255 Bq per gram of carbon.
(a) What fraction of carbon atoms were 14C?
(b) An archaeological specimen containing 500 mg of carbon, shows 174 decays in one hour. What is the age of the specimen, assuming that its activity per unit mass of carbon when the specimen died was equal to the average value of the air? The half-life of 14C is 5730 years.
Two radioactive materials X1 and X2 have decay constants 10λ and λ respectively. If initially, they have the same number of nuclei, then the ratio of the number of nuclei of X1 to that of X2 will belie after a time.
'Half-life' of a radioactive substance accounts for ______.
The half-life of a radioactive sample undergoing `alpha` - decay is 1.4 x 1017 s. If the number of nuclei in the sample is 2.0 x 1021, the activity of the sample is nearly ____________.
Two radioactive materials Y1 and Y2 have decay constants '5`lambda`' and `lambda` respectively. Initially they have same number of nuclei. After time 't', the ratio of number of nuclei of Y1 to that of Y2 is `1/"e"`, then 't' is equal to ______.
Draw a graph showing the variation of decay rate with number of active nuclei.
The activity R of an unknown radioactive nuclide is measured at hourly intervals. The results found are tabulated as follows:
| t (h) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| R (MBq) | 100 | 35.36 | 12.51 | 4.42 | 1.56 |
- Plot the graph of R versus t and calculate the half-life from the graph.
- Plot the graph of ln `(R/R_0)` versus t and obtain the value of half-life from the graph.
