Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The decay constant of a radioactive sample is λ. The half-life and the average-life of the sample are respectively
Options
1/λ and (In 2/λ)
(In 2/λ) and 1/λ
λ(In 2) and 1/λ
λ/(In 2) and 1/λ.
Solution
(ln 2/λ) and 1/λ
The half-life of a radioactive sample `(t_(1"/"2))` is defined as the time elapsed before half the active nuclei decays.
Let the initial number of the active nuclei present in the sample be `N_0` .
`N_0/2 = N_0e^(-lambdat_"1/2")`
⇒ `t_"1/2" = ("In 2")/lambda`
Average life of the nuclei, `t_(av) = S/N_0 = 1/lambda`
Here, S is the sum of all the lives of all the N nuclei that were active at t = 0 and `lambda` is the decay constant of the sample.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Obtain the relation between the decay constant and half life of a radioactive sample.
The normal activity of living carbon-containing matter is found to be about 15 decays per minute for every gram of carbon. This activity arises from the small proportion of radioactive `""_6^14"C"` present with the stable carbon isotope `""_6^12"C"`. When the organism is dead, its interaction with the atmosphere (which maintains the above equilibrium activity) ceases and its activity begins to drop. From the known half-life (5730 years) of `""_6^14"C"` and the measured activity, the age of the specimen can be approximately estimated. This is the principle of `""_6^14"C"` dating used in archaeology. Suppose a specimen from Mohenjodaro gives an activity of 9 decays per minute per gram of carbon. Estimate the approximate age of the Indus-Valley civilisation.
The half-life of `""_38^90 "Sr"` is 28 years. What is the disintegration rate of 15 mg of this isotope?
The Q value of a nuclear reaction \[\ce{A + b → C + d}\] is defined by
Q = [ mA+ mb− mC− md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^1_1H + ^3_1H -> ^2_1H + ^2_1H}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12"C")` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
The Q value of a nuclear reaction A + b → C + d is defined by
Q = [mA+ mb − mC − md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^12_6C + ^12_6C ->^20_10Ne + ^4_2He}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12C)` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
(a) Derive the relation between the decay constant and half life of a radioactive substance.
(b) A radioactive element reduces to 25% of its initial mass in 1000 years. Find its half life.
A radioactive nucleus ‘A’ undergoes a series of decays according to the following scheme:
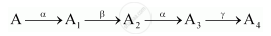
The mass number and atomic number of A are 180 and 72 respectively. What are these numbers for A4?
Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the beta particle emitted in the following decay scheme:
12N → 12C* + e+ + v
12C* → 12C + γ (4.43MeV).
The atomic mass of 12N is 12.018613 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
When charcoal is prepared from a living tree, it shows a disintegration rate of 15.3 disintegrations of 14C per gram per minute. A sample from an ancient piece of charcoal shows 14C activity to be 12.3 disintegrations per gram per minute. How old is this sample? Half-life of 14C is 5730 y.
Obtain a relation between the half-life of a radioactive substance and decay constant (λ).
Define one Becquerel.
Disintegration rate of a sample is 1010 per hour at 20 hours from the start. It reduces to 6.3 x 109 per hour after 30 hours. Calculate its half-life and the initial number of radioactive atoms in the sample.
The isotope \[\ce{^57Co}\] decays by electron capture to \[\ce{^57Fe}\] with a half-life of 272 d. The \[\ce{^57Fe}\] nucleus is produced in an excited state, and it almost instantaneously emits gamma rays.
(a) Find the mean lifetime and decay constant for 57Co.
(b) If the activity of a radiation source 57Co is 2.0 µCi now, how many 57Co nuclei does the source contain?
c) What will be the activity after one year?
'Half-life' of a radioactive substance accounts for ______.
Two electrons are ejected in opposite directions from radioactive atoms in a sample of radioactive material. Let c denote the speed of light. Each electron has a speed of 0.67 c as measured by an observer in the laboratory. Their relative velocity is given by ______.
If 10% of a radioactive material decay in 5 days, then the amount of original material left after 20 days is approximately :
Samples of two radioactive nuclides A and B are taken. λA and λB are the disintegration constants of A and B respectively. In which of the following cases, the two samples can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time?
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA = λB.
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is twice the initial rate of decay of A and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is the same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λB < λA.
Draw a graph showing the variation of decay rate with number of active nuclei.
