Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The decay constant of a radioactive sample is λ. The half-life and the average-life of the sample are respectively
विकल्प
1/λ and (In 2/λ)
(In 2/λ) and 1/λ
λ(In 2) and 1/λ
λ/(In 2) and 1/λ.
उत्तर
(ln 2/λ) and 1/λ
The half-life of a radioactive sample `(t_(1"/"2))` is defined as the time elapsed before half the active nuclei decays.
Let the initial number of the active nuclei present in the sample be `N_0` .
`N_0/2 = N_0e^(-lambdat_"1/2")`
⇒ `t_"1/2" = ("In 2")/lambda`
Average life of the nuclei, `t_(av) = S/N_0 = 1/lambda`
Here, S is the sum of all the lives of all the N nuclei that were active at t = 0 and `lambda` is the decay constant of the sample.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why is it found experimentally difficult to detect neutrinos in nuclear β-decay?
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to a) 3.125%, b) 1% of its original value?
The normal activity of living carbon-containing matter is found to be about 15 decays per minute for every gram of carbon. This activity arises from the small proportion of radioactive `""_6^14"C"` present with the stable carbon isotope `""_6^12"C"`. When the organism is dead, its interaction with the atmosphere (which maintains the above equilibrium activity) ceases and its activity begins to drop. From the known half-life (5730 years) of `""_6^14"C"` and the measured activity, the age of the specimen can be approximately estimated. This is the principle of `""_6^14"C"` dating used in archaeology. Suppose a specimen from Mohenjodaro gives an activity of 9 decays per minute per gram of carbon. Estimate the approximate age of the Indus-Valley civilisation.
The radionuclide 11C decays according to
\[\ce{^11_6C -> ^11_5B + e+ + \text{v}}\] : T1/2 = 20.3 min
The maximum energy of the emitted positron is 0.960 MeV.
Given the mass values: `"m"(""_6^11"C") = 11.011434 u and "m"(""_6^11"B") = 11.009305 "u"`
Calculate Q and compare it with the maximum energy of the positron emitted.
The Q value of a nuclear reaction \[\ce{A + b → C + d}\] is defined by
Q = [ mA+ mb− mC− md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^1_1H + ^3_1H -> ^2_1H + ^2_1H}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12"C")` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an α-particle. Consider the following decay processes:
\[\ce{^223_88Ra -> ^209_82Pb + ^14_6C}\]
\[\ce{^223_88 Ra -> ^219_86 Rn + ^4_2He}\]
Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed.
A radioactive nucleus 'A' undergoes a series of decays as given below:
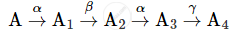
The mass number and atomic number of A2 are 176 and 71 respectively. Determine the mass and atomic numbers of A4 and A.
Define the activity of a given radioactive substance. Write its S.I. unit.
The radioactive isotope D decays according to the sequence
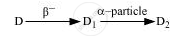
If the mass number and atomic number of D2 are 176 and 71 respectively, what is (i) the mass number (ii) atomic number of D?
28Th emits an alpha particle to reduce to 224Ra. Calculate the kinetic energy of the alpha particle emitted in the following decay:
`""^228"Th" → ""^224"Ra"^(∗) + alpha`
`""^224"Ra"^(∗) → ""^224"Ra" + γ (217 "keV")`.
Atomic mass of 228Th is 228.028726 u, that of 224Ra is 224.020196 u and that of `""_2^4H` is 4.00260 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
When charcoal is prepared from a living tree, it shows a disintegration rate of 15.3 disintegrations of 14C per gram per minute. A sample from an ancient piece of charcoal shows 14C activity to be 12.3 disintegrations per gram per minute. How old is this sample? Half-life of 14C is 5730 y.
Define the term 'decay constant' of a radioactive sample. The rate of disintegration of a given radioactive nucleus is 10000 disintegrations/s and 5,000 disintegrations/s after 20 hr. and 30 hr. respectively from start. Calculate the half-life and the initial number of nuclei at t= 0.
What is the amount of \[\ce{_27^60Co}\] necessary to provide a radioactive source of strength 10.0 mCi, its half-life being 5.3 years?
The half-life of a radioactive nuclide is 20 hrs. The fraction of the original activity that will remain after 40 hrs is ______.
Samples of two radioactive nuclides A and B are taken. λA and λB are the disintegration constants of A and B respectively. In which of the following cases, the two samples can simultaneously have the same decay rate at any time?
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA = λB.
- Initial rate of decay of A is twice the initial rate of decay of B and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is twice the initial rate of decay of A and λA > λB.
- Initial rate of decay of B is the same as the rate of decay of A at t = 2h and λB < λA.
Which sample, A or B shown in figure has shorter mean-life?
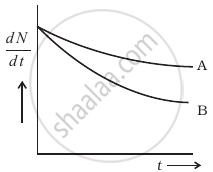
A piece of wood from the ruins of an ancient building was found to have a 14C activity of 12 disintegrations per minute per gram of its carbon content. The 14C activity of the living wood is 16 disintegrations per minute per gram. How long ago did the tree, from which the wooden sample came, die? Given half-life of 14C is 5760 years.
Sometimes a radioactive nucleus decays into a nucleus which itself is radioactive. An example is :
\[\ce{^38Sulphur ->[half-life][= 2.48h] ^{38}Cl ->[half-life][= 0.62h] ^38Air (stable)}\]
Assume that we start with 1000 38S nuclei at time t = 0. The number of 38Cl is of count zero at t = 0 and will again be zero at t = ∞ . At what value of t, would the number of counts be a maximum?
The activity R of an unknown radioactive nuclide is measured at hourly intervals. The results found are tabulated as follows:
| t (h) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| R (MBq) | 100 | 35.36 | 12.51 | 4.42 | 1.56 |
- Plot the graph of R versus t and calculate the half-life from the graph.
- Plot the graph of ln `(R/R_0)` versus t and obtain the value of half-life from the graph.
What is the half-life period of a radioactive material if its activity drops to 1/16th of its initial value of 30 years?
