Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The Q value of a nuclear reaction \[\ce{A + b → C + d}\] is defined by
Q = [ mA+ mb− mC− md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^1_1H + ^3_1H -> ^2_1H + ^2_1H}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12"C")` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
उत्तर
The given nuclear reaction is:
\[\ce{^1_1H + ^3_1H -> ^2_1H + ^2_1H}\]
It is given that:
Atomic mass `m(""_1^1"H")` = 1.007825 u
Atomic mass `m(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
Atomic mass `m(""_1^2"H") = 2.014102 u`
According to the question, the Q-value of the reaction can be written as:
Q = `["m"(""_1^1"H") + "m"(""_1^3"H") - 2"m"(""_1^2"H")]"c"^2`
Q = (- 0.00433 c2)u
But 1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2
`= [1.007825 + 3.016049 - 2 xx 2.014102]c^2`
`"Q" = - 0.00433 xx 931.5 = - 4.0334` MeV
The negative Q-value of the reaction shows that the reaction is endothermic.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the law of radioactive decay.
Obtain the relation between the decay constant and half life of a radioactive sample.
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to a) 3.125%, b) 1% of its original value?
The Q value of a nuclear reaction A + b → C + d is defined by
Q = [mA+ mb − mC − md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^12_6C + ^12_6C ->^20_10Ne + ^4_2He}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12C)` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
A radioactive nucleus 'A' undergoes a series of decays as given below:
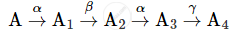
The mass number and atomic number of A2 are 176 and 71 respectively. Determine the mass and atomic numbers of A4 and A.
Using the equation `N = N_0e^(-lambdat)` obtain the relation between half-life (T) and decay constant (`lambda`) of a radioactive substance.
Lithium (Z = 3) has two stable isotopes 6Li and 7Li. When neutrons are bombarded on lithium sample, electrons and α-particles are ejected. Write down the nuclear process taking place.
The masses of 11C and 11B are respectively 11.0114 u and 11.0093 u. Find the maximum energy a positron can have in the β*-decay of 11C to 11B.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
Obtain a relation between the half-life of a radioactive substance and decay constant (λ).
Define the term 'decay constant' of a radioactive sample. The rate of disintegration of a given radioactive nucleus is 10000 disintegrations/s and 5,000 disintegrations/s after 20 hr. and 30 hr. respectively from start. Calculate the half-life and the initial number of nuclei at t= 0.
The isotope \[\ce{^57Co}\] decays by electron capture to \[\ce{^57Fe}\] with a half-life of 272 d. The \[\ce{^57Fe}\] nucleus is produced in an excited state, and it almost instantaneously emits gamma rays.
(a) Find the mean lifetime and decay constant for 57Co.
(b) If the activity of a radiation source 57Co is 2.0 µCi now, how many 57Co nuclei does the source contain?
c) What will be the activity after one year?
Obtain an expression for the decay law of radioactivity. Hence show that the activity A(t) =λNO e-λt.
'Half-life' of a radioactive substance accounts for ______.
The half-life of a radioactive sample undergoing `alpha` - decay is 1.4 x 1017 s. If the number of nuclei in the sample is 2.0 x 1021, the activity of the sample is nearly ____________.
After 1 hour, `(1/8)^"th"` of the initial mass of a certain radioactive isotope remains undecayed. The half-life of the isotopes is ______.
Two radioactive materials Y1 and Y2 have decay constants '5`lambda`' and `lambda` respectively. Initially they have same number of nuclei. After time 't', the ratio of number of nuclei of Y1 to that of Y2 is `1/"e"`, then 't' is equal to ______.
The half-life of the radioactive substance is 40 days. The substance will disintegrate completely in
Suppose we consider a large number of containers each containing initially 10000 atoms of a radioactive material with a half life of 1 year. After 1 year ______.
The half-life of `""_82^210Pb` is 22.3 y. How long will it take for its activity 0 30% of the initial activity?
