Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Lithium (Z = 3) has two stable isotopes 6Li and 7Li. When neutrons are bombarded on lithium sample, electrons and α-particles are ejected. Write down the nuclear process taking place.
उत्तर
The nuclear process taking place is shown below.
`""_8^6"L_i" + n → ""_3^7L_i`
`""_3^7L_i + n → ""_3^8L_i → ""_4^8"Be" + barv + e^-`
`""_4^8"Be" → ""_2^4"He" + ""_2^4"He"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(a) Write the basic nuclear process involved in the emission of β+ in a symbolic form, by a radioactive nucleus.
(b) In the reactions given below:
(i)`""_16^11C->_y^zB+x+v`
(ii)`""_6^12C+_6^12C->_a^20 Ne + _b^c He`
Find the values of x, y, and z and a, b and c.
State the law of radioactive decay.
How is the mean life of a given radioactive nucleus related to the decay constant?
Write symbolically the process expressing the β+ decay of `""_11^22Na`. Also write the basic nuclear process underlying this decay.
The half-life of `""_38^90 "Sr"` is 28 years. What is the disintegration rate of 15 mg of this isotope?
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an α-particle. Consider the following decay processes:
\[\ce{^223_88Ra -> ^209_82Pb + ^14_6C}\]
\[\ce{^223_88 Ra -> ^219_86 Rn + ^4_2He}\]
Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed.
A radioactive nucleus 'A' undergoes a series of decays as given below:
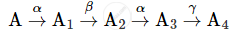
The mass number and atomic number of A2 are 176 and 71 respectively. Determine the mass and atomic numbers of A4 and A.
Define 'activity' of a radioactive substance ?
In a radioactive decay, neither the atomic number nor the mass number changes. Which of the following particles is emitted in the decay?
The decay constant of a radioactive sample is λ. The half-life and the average-life of the sample are respectively
The decay constant of `""_80^197`Hg (electron capture to `""_79^197`Au) is 1.8 × 10−4 S−1. (a) What is the half-life? (b) What is the average-life? (c) How much time will it take to convert 25% of this isotope of mercury into gold?
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
Consider the situation of the previous problem. Suppose the production of the radioactive isotope starts at t = 0. Find the number of active nuclei at time t.
Obtain a relation between the half-life of a radioactive substance and decay constant (λ).
Identify the nature of the radioactive radiations emitted in each step of the decay process given below.
`""_Z^A X -> _Z^A _-1^-4 Y ->_Z^A _-1^-4 W`
A radioactive substance disintegrates into two types of daughter nuclei, one type with disintegration constant λ1 and the other type with disintegration constant λ2 . Determine the half-life of the radioactive substance.
After 1 hour, `(1/8)^"th"` of the initial mass of a certain radioactive isotope remains undecayed. The half-life of the isotopes is ______.
Two radioactive materials Y1 and Y2 have decay constants '5`lambda`' and `lambda` respectively. Initially they have same number of nuclei. After time 't', the ratio of number of nuclei of Y1 to that of Y2 is `1/"e"`, then 't' is equal to ______.
What is the half-life period of a radioactive material if its activity drops to 1/16th of its initial value of 30 years?
