Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The decay constant of `""_80^197`Hg (electron capture to `""_79^197`Au) is 1.8 × 10−4 S−1. (a) What is the half-life? (b) What is the average-life? (c) How much time will it take to convert 25% of this isotope of mercury into gold?
उत्तर
Given :-
Decay Constant of `""_80^197"Hg" , lambda = 1.8 xx 10^-4 "s"^-1`
(a)
Half-life, `T_"1/2" = 0.693/lambda`
`⇒ T_"1/2" = 0.693/(1.8 xx 10^-4)`
= 3850 s=64 minutes
(b)
Average life, `T_(av) = T_"1/2"/0.693`
`= 64/0.693`
= 92 minutes
(c)
Number of active nuclei of mercury at t = 0 = N0 = 100
Active nuclei of mercury left after conversion of 25% isotope of mercury into gold = N = 75
Now , `N/N_0 = e^(-lambda t)`
Here,
N = Number of inactive nuclei
`N_0` = Number of nuclei at t = 0
`lambda =` Disintegration constant
On substituting the values, we get
`75/100 = e^(-lambdat)`
`⇒ 0.75 = e^(-lambda x)`
`⇒ "In" 0.75 = - lambda t`
`⇒ t = ("In" 0.75)/-0.00018`
= 1600 s
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The decay constant of radioactive substance is 4.33 x 10-4 per year. Calculate its half life period.
Write symbolically the process expressing the β+ decay of `""_11^22Na`. Also write the basic nuclear process underlying this decay.
Why is it found experimentally difficult to detect neutrinos in nuclear β-decay?
The half-life of `""_38^90 "Sr"` is 28 years. What is the disintegration rate of 15 mg of this isotope?
The Q value of a nuclear reaction \[\ce{A + b → C + d}\] is defined by
Q = [ mA+ mb− mC− md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^1_1H + ^3_1H -> ^2_1H + ^2_1H}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12"C")` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
A source contains two phosphorous radio nuclides `""_15^32"P"` (T1/2 = 14.3d) and `""_15^33"P"` (T1/2 = 25.3d). Initially, 10% of the decays come from `""_15^33"P"`. How long one must wait until 90% do so?
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an α-particle. Consider the following decay processes:
\[\ce{^223_88Ra -> ^209_82Pb + ^14_6C}\]
\[\ce{^223_88 Ra -> ^219_86 Rn + ^4_2He}\]
Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed.
Represent Radioactive Decay curve using relation `N = N_o e^(-lambdat)` graphically
Using the equation `N = N_0e^(-lambdat)` obtain the relation between half-life (T) and decay constant (`lambda`) of a radioactive substance.
Define 'activity' of a radioactive substance ?
In a given sample, two radioisotopes, A and B, are initially present in the ration of 1 : 4. The half lives of A and B are respectively 100 years and 50 years. Find the time after which the amounts of A and B become equal.
The radioactive isotope D decays according to the sequence
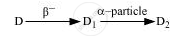
If the mass number and atomic number of D2 are 176 and 71 respectively, what is (i) the mass number (ii) atomic number of D?
The masses of 11C and 11B are respectively 11.0114 u and 11.0093 u. Find the maximum energy a positron can have in the β*-decay of 11C to 11B.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
57Co decays to 57Fe by β+- emission. The resulting 57Fe is in its excited state and comes to the ground state by emitting γ-rays. The half-life of β+- decay is 270 days and that of the γ-emissions is 10−8 s. A sample of 57Co gives 5.0 × 109 gamma rays per second. How much time will elapse before the emission rate of gamma rays drops to 2.5 × 109per second?
When charcoal is prepared from a living tree, it shows a disintegration rate of 15.3 disintegrations of 14C per gram per minute. A sample from an ancient piece of charcoal shows 14C activity to be 12.3 disintegrations per gram per minute. How old is this sample? Half-life of 14C is 5730 y.
Define one Becquerel.
Before the year 1900 the activity per unit mass of atmospheric carbon due to the presence of 14C averaged about 0.255 Bq per gram of carbon.
(a) What fraction of carbon atoms were 14C?
(b) An archaeological specimen containing 500 mg of carbon, shows 174 decays in one hour. What is the age of the specimen, assuming that its activity per unit mass of carbon when the specimen died was equal to the average value of the air? The half-life of 14C is 5730 years.
Two radioactive materials X1 and X2 have decay constants 10λ and λ respectively. If initially, they have the same number of nuclei, then the ratio of the number of nuclei of X1 to that of X2 will belie after a time.
If 10% of a radioactive material decay in 5 days, then the amount of original material left after 20 days is approximately :
A piece of wood from the ruins of an ancient building was found to have a 14C activity of 12 disintegrations per minute per gram of its carbon content. The 14C activity of the living wood is 16 disintegrations per minute per gram. How long ago did the tree, from which the wooden sample came, die? Given half-life of 14C is 5760 years.
