Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
28Th emits an alpha particle to reduce to 224Ra. Calculate the kinetic energy of the alpha particle emitted in the following decay:
`""^228"Th" → ""^224"Ra"^(∗) + alpha`
`""^224"Ra"^(∗) → ""^224"Ra" + γ (217 "keV")`.
Atomic mass of 228Th is 228.028726 u, that of 224Ra is 224.020196 u and that of `""_2^4H` is 4.00260 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
उत्तर
Given:-
Atomic mass of 228Th, m(228Th) = 228.028726 u
Atomic mass of 224Ra, m(224Ra) = 224.020196 u
Atomic mass of `""_2^4H, m(""_2^4H) = 4.00260 "u"`
Mass of 224Ra = 224.020196 × 931 + 0.217 MeV = 208563.0195 MeV
Kinetic energy of alpha particle, K = `[m(""^228"Th") - [m(""^224"Ra") + m(""_2^4"H")]]c^2`
= (228.028726 × 931) − [(208563.0195 + 4.00260 × 931]
= 5.30383 MeV = 5.304 MeV
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. How long will it take the activity to reduce to a) 3.125%, b) 1% of its original value?
The radionuclide 11C decays according to
\[\ce{^11_6C -> ^11_5B + e+ + \text{v}}\] : T1/2 = 20.3 min
The maximum energy of the emitted positron is 0.960 MeV.
Given the mass values: `"m"(""_6^11"C") = 11.011434 u and "m"(""_6^11"B") = 11.009305 "u"`
Calculate Q and compare it with the maximum energy of the positron emitted.
A radioactive nucleus 'A' undergoes a series of decays as given below:
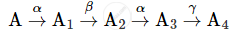
The mass number and atomic number of A2 are 176 and 71 respectively. Determine the mass and atomic numbers of A4 and A.
Using the equation `N = N_0e^(-lambdat)` obtain the relation between half-life (T) and decay constant (`lambda`) of a radioactive substance.
Define 'activity' of a radioactive substance ?
In a given sample, two radioisotopes, A and B, are initially present in the ration of 1 : 4. The half lives of A and B are respectively 100 years and 50 years. Find the time after which the amounts of A and B become equal.
A radioactive nucleus ‘A’ undergoes a series of decays according to the following scheme:
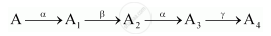
The mass number and atomic number of A are 180 and 72 respectively. What are these numbers for A4?
The decay constant of `""_80^197`Hg (electron capture to `""_79^197`Au) is 1.8 × 10−4 S−1. (a) What is the half-life? (b) What is the average-life? (c) How much time will it take to convert 25% of this isotope of mercury into gold?
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
57Co decays to 57Fe by β+- emission. The resulting 57Fe is in its excited state and comes to the ground state by emitting γ-rays. The half-life of β+- decay is 270 days and that of the γ-emissions is 10−8 s. A sample of 57Co gives 5.0 × 109 gamma rays per second. How much time will elapse before the emission rate of gamma rays drops to 2.5 × 109per second?
What is the amount of \[\ce{_27^60Co}\] necessary to provide a radioactive source of strength 10.0 mCi, its half-life being 5.3 years?
Disintegration rate of a sample is 1010 per hour at 20 hours from the start. It reduces to 6.3 x 109 per hour after 30 hours. Calculate its half-life and the initial number of radioactive atoms in the sample.
Obtain an expression for the decay law of radioactivity. Hence show that the activity A(t) =λNO e-λt.
Two radioactive materials X1 and X2 have decay constants 10λ and λ respectively. If initially, they have the same number of nuclei, then the ratio of the number of nuclei of X1 to that of X2 will belie after a time.
The half-life of a radioactive sample undergoing `alpha` - decay is 1.4 x 1017 s. If the number of nuclei in the sample is 2.0 x 1021, the activity of the sample is nearly ____________.
Two radioactive materials Y1 and Y2 have decay constants '5`lambda`' and `lambda` respectively. Initially they have same number of nuclei. After time 't', the ratio of number of nuclei of Y1 to that of Y2 is `1/"e"`, then 't' is equal to ______.
What percentage of radioactive substance is left after five half-lives?
Suppose we consider a large number of containers each containing initially 10000 atoms of a radioactive material with a half life of 1 year. After 1 year ______.
Sometimes a radioactive nucleus decays into a nucleus which itself is radioactive. An example is :
\[\ce{^38Sulphur ->[half-life][= 2.48h] ^{38}Cl ->[half-life][= 0.62h] ^38Air (stable)}\]
Assume that we start with 1000 38S nuclei at time t = 0. The number of 38Cl is of count zero at t = 0 and will again be zero at t = ∞ . At what value of t, would the number of counts be a maximum?
