Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe the total degrees of freedom for monoatomic molecule, diatomic molecule and triatomic molecule.
Solution
Monoatomic molecule: A monoatomic molecule has only three translational degrees of freedom by virtue of its nature.
∴ f = 3
Example: Helium, Neon, Argon
Diatomic molecule: There are two cases.
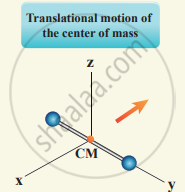
(i) At Normal temperature: A molecule of a diatomic gas consists of two atoms bound to each other by a force of attraction, the center of mass lies in the center of the diatomic molecule. So, the motion of the center of mass requires three translational degrees of freedom.
In addition, the diatomic molecule can be rotated about three mutually perpendicular axes.
Degree of freedom of diatomic molecule
In addition, the diatomic molecule can be rotated about three mutually perpendicular axes.

But the moment of inertia about its own axis of rotation is negligible. Hence, it has only two rotational degrees of freedom. So totally there are five degrees of freedom.
f = 5
(ii) At high temperature: At a very high temperature such as 5000 K, the diatomic molecules possess additional two degrees of freedom due to vibrational motion [one due to kinetic energy of vibration and the other is due to potential energy].
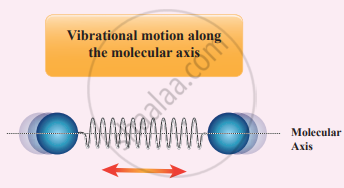
So totally there are seven degrees of freedom.
f = 7
Example: Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen.
(i) Linear triatomic molecule: The linear triatomic molecule has three translational degrees of freedom. It has two rotational degrees of freedom because it is similar to a diatomic molecule except there is an additional atom at the center.
At normal temperature, linear triatomic molecules will have five degrees of freedom. It has two additional vibrational degrees of freedom at high temperatures.
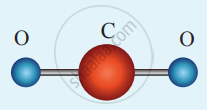
A linear triatomic molecule
So a linear triatomic molecule has seven degrees of freedom.
Example: Carbon dioxide.
(ii) Non-linear triatomic molecule: It has three translational degrees of freedom and three rotational degrees of freedom about three mutually orthogonal axes. So, the total degrees of freedom.
f = 6
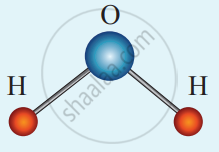
A non-linear triatomic molecule
Example: Water, Sulphur dioxide.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A container has one mole of the monoatomic ideal gas. Each molecule has f degrees of freedom. What is the ratio of γ = `"C"_"p"/"C"_"v"`?
A sample of gas consists of μ1 moles of monoatomic molecules, μ2 moles of diatomic molecules and μ3 moles of linear triatomic molecules. The gas is kept at a high temperature. What is the total number of degrees of freedom?
Define the term degrees of freedom.
Derive the ratio of two specific heat capacities of monoatomic, diatomic and triatomic molecules.
A gas made of a mixture of 2 moles of oxygen and 4 moles of argon at temperature T. Calculate the energy of the gas in terms of RT. Neglect the vibrational modes.
Two monoatomic gas A and B occupying the same volume V are at the same temperature T and pressure P. If they are mixed, the resulting mixture has volume V and temperature T. The pressure of the mixture is:
Which of the following statement given below are correct for monoatomic gas?
I. Cv = `3/2 "R"`
II. Cp = `5/2 "R"`
III. Cp − Cv = 2R
IV. `"C"_"p"/"C"_"v" = 5/3`
A ballon has 5.0 g mole of helium at 7°C. Calculate
- the number of atoms of helium in the balloon
- the total internal energy of the system.
A gas has n degrees of freedom. The ratio of the specific heat of the gas at constant volume to the specific heat of the gas at constant pressure will be ______.
An ideal gas has molecules with 5 degrees of freedom. The ratio of specific heats at constant pressure (CP) and at constant volume (Cv) is ______.
